Linux中Makefile工具的简单使用
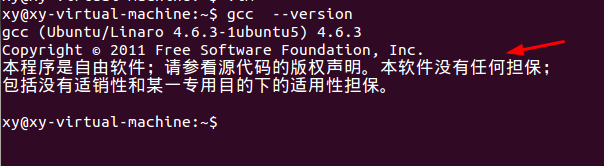
1、Ctrl+Alt+T打开终端,查看GCC和VIM(vim-nox)软件包是否安装成功,可输入gcc --version或vim查看版本号确认安装成功。

2、使用VIM编辑器编写Makefile文件:
(1)首先编写一个““Hello,World!”程序”
建立一个hello_test.c程序,源代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
printf("Hello,World!\n"); /* 打印字符串Hello,World!到屏幕 */
return 0;
}
(2)在hello_test.c所在目录:输入vi Makefile(vim Makefile)
(3)输入程序:
hello_test : hello_test.c
gcc -o hello_test hello_test.c
clean :
rm -fr hello_test *.o *.core
(4)按下Esc键后输入:wq保存文件并退出。




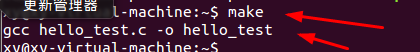
3、对hello_test.c编译:make
(1)如果没错,则屏幕弹出“gcc –o hello_test hello_test.c”
(2)找到hello_test可执行文件(绿色)
(3)执行文件:./hello_test

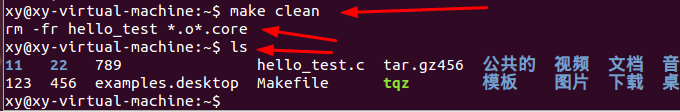
4、通过make的参数指定执行clean依赖关系:
输入make clean,查看hello_test可执行文件的变化。

1、使用vim编写mytool1.c 、mytool2.c、main.c、mytool1.h、mytool2.h、makefile文件。
mytool1.c
#include “mytool1.h”
#include<stdio.h>
void mytool1_print(char *print_str)
{:
printf(“This is mytool1 print:%s”,print_str);
}
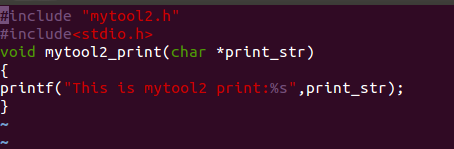
mytool2.c
#include “mytool2.h”
#include<stdio.h>
void mytool2 _print(char *print_str)
{
printf(“This is mytool2 print:%s”,print_str);
}
main.c
#include “mytool1.h”
#include “mytool2.h”
int main()
{
mytool1_print(“hello mytool1!”);
mytool2_print(“hello mytool2!”);
return 0;
}
mytool1.h
#ifndef _MYTOOL_1_H
#define _MYTOOL_1_H
void mytool1_print(char *print_str);
#endif
mytool2.h
#ifndef _MYTOOL_2_H
#define _MYTOOL_2_H
void mytool2_print(char *print_str);
#endif
makefile
target: mytool1.o mytool2.o main.o
gcc -g -o target mytool1.o mytool2.o main.o
mytool1.o: mytool1.c mytool1.h
gcc -g -c mytool1.c
mytool2.o: mytool2.c mytool2.h
gcc -g -c mytool2.c
main.o: main.c mytool1.h mytool2.h
gcc -g -c main.c





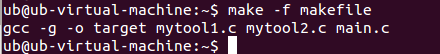
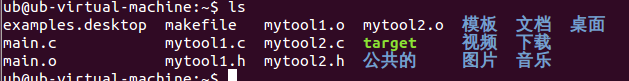
2、(1)执行make,
(2)查看文件ls,可以看见生成了一个可执行文件target
(3)执行文件显示结果:./target


1、更改makefile文件
改进一:
SRCS=mytool1.c mytool2.c main.c
PROG=target
CC=gcc
CFLAGS=-g
OBJS=$(SRCS:.c=.o)
$(PROG):$(OBJS)
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -o $@ $^
$(OBJS): mytool1.h mytool2.h
clean:
rm –f $(OBJS) $(PROG)

2、先删除可执行文件target,用ls查看文件是否删除成功,在执行make,用ls查看发现生成一个可执行文件target,执行文件。执行make clean命令,用ls查看文件的变化。






3、改进二:
trget:main.o mytool1.o mytool2.o
gcc -g -o target main.o mytool1.o mytool2.o
main.o mytool1.o mytool2.o: mytool1.h mytool2.h

4、先删除可执行文件target,用ls查看文件是否删除成功,在执行make,用ls查看发现生成一个可执行文件target,执行文件。