matlab的示例
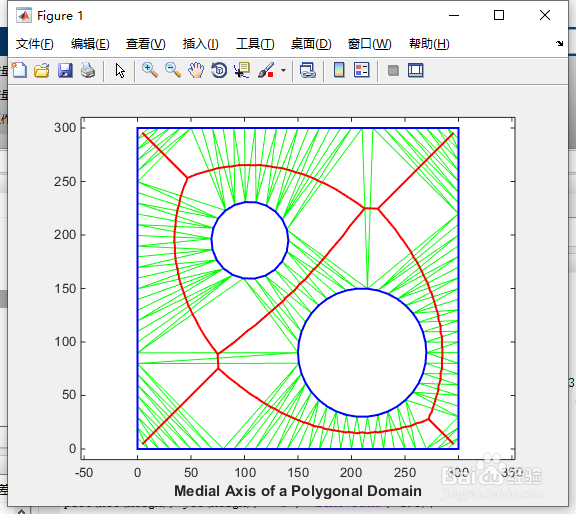
1、示例一:计算多边形域的近似中间。
本示例说明了如何使用约束的Delaunay三角剖分来创建多边形域的近似中间轴。
多边形的中间轴由多边形内部最大磁盘中心的轨迹定义。
程序如下:
% Construct a constrained Delaunay triangulation of a sample of points
% on the domain boundary.
load trimesh2d
dt = delaunayTriangulation(x,y,Constraints);
inside = dt.isInterior();
% Construct a triangulation to represent the domain triangles.
tr = triangulation(dt(inside, :), dt.Points);
% Construct a set of edges that join the circumcenters of neighboring
% triangles; the additional logic constructs a unique set of such edges.
numt = size(tr,1);
T = (1:numt)';
neigh = tr.neighbors();
cc = tr.circumcenter();
xcc = cc(:,1);
ycc = cc(:,2);
idx1 = T < neigh(:,1);
idx2 = T < neigh(:,2);
idx3 = T < neigh(:,3);
neigh = [T(idx1) neigh(idx1,1); T(idx2) neigh(idx2,2); T(idx3) neigh(idx3,3)]';
% Plot the domain triangles in green, the domain boundary in blue and the
% medial axis in red.
clf;
triplot(tr, 'g');
hold on;
plot(xcc(neigh), ycc(neigh), '-r', 'LineWidth', 1.5);
axis([-10 310 -10 310]);
axis equal;
plot(x(Constraints'),y(Constraints'), '-b', 'LineWidth', 1.5);
xlabel('Medial Axis of a Polygonal Domain', 'fontweight','b');
hold off;
按“Enter”键。
如图1所示。
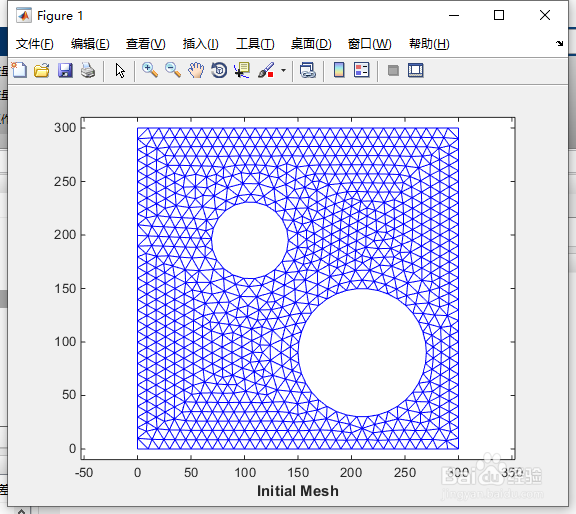
2、示例二:将2D网格变形为修改后的边界
此示例显示如何变形2D域的网格以适应对域边界的修改。
步骤1:加载数据。 要变形的网格由trife,xfe,yfe定义,它是面顶点格式的三角剖分。
程序如下:
load trimesh2d
clf;
triplot(trife,xfe,yfe);
axis equal;
axis([-10 310 -10 310]);
axis equal;
xlabel('Initial Mesh', 'fontweight','b');
按“Enter”键。
如图2所示。
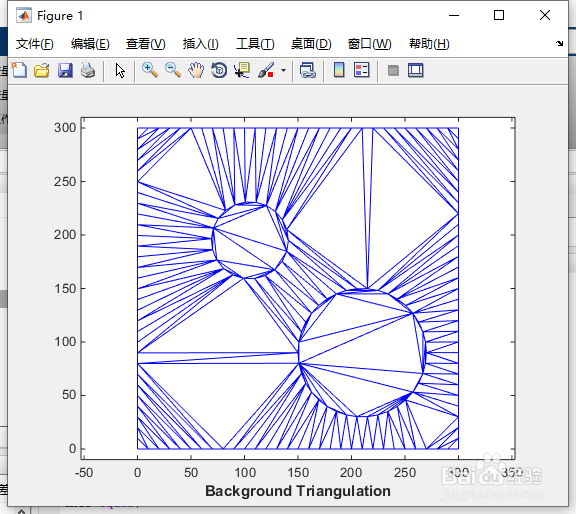
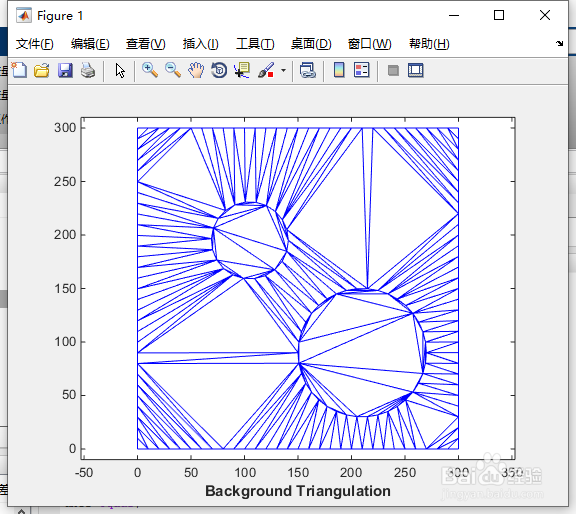
3、步骤2:构造背景三角剖分-代表网格边界的点集的约束Delaunay三角剖分。 对于网格的每个顶点,计算一个描述符,以定义其相对于背景三角剖分的位置。 描述子是包围的三角形以及相对于该三角形的重心坐标。
程序入下:
dt = delaunayTriangulation(x,y,Constraints);
clf;
triplot(dt);
axis equal;
axis([-10 310 -10 310]);
axis equal;
xlabel('Background Triangulation', 'fontweight','b');
descriptors.tri = pointLocation(dt,xfe, yfe);
descriptors.baryCoords = cartesianToBarycentric(dt,descriptors.tri, [xfe yfe]);
按“Enter”键。
如图3所示。
4、步骤3:编辑背景三角剖分,以将所需的修改合并到域边界。
程序如下:
cc1 = [210 90];
circ1 = (143:180)';
x(circ1) = (x(circ1)-cc1(1))*0.6 + cc1(1);
y(circ1) = (y(circ1)-cc1(2))*0.6 + cc1(2);
tr = triangulation(dt(:,:),x,y);
clf;
triplot(tr);
axis([-10 310 -10 310]);
axis equal;
xlabel('Edited Background Triangulation - Hole Size Reduced', 'fontweight','b');
按“Enter”键。
如图4所示。
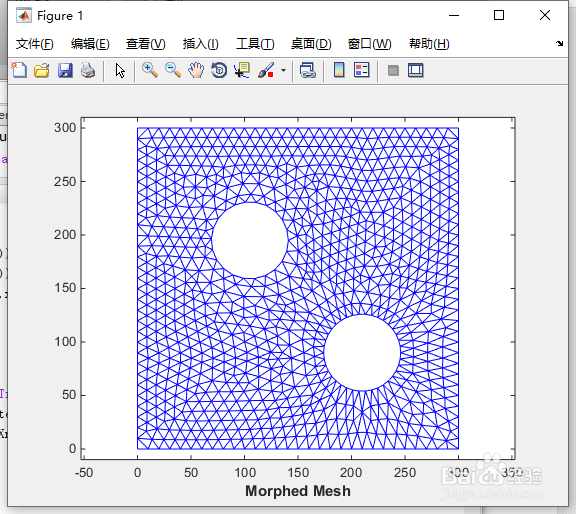
5、步骤4:使用变形的背景三角剖分作为评估的基础,将描述符转换回笛卡尔坐标。
程序入下:
Xnew = barycentricToCartesian(tr,descriptors.tri, descriptors.baryCoords);
tr = triangulation(trife, Xnew);
clf;
triplot(tr);
axis([-10 310 -10 310]);
axis equal;
xlabel('Morphed Mesh', 'fontweight','b');
按“Enter”键。
如图5所示。