python中numpy的数组数学运算
1、元素运算:numpy中数组中对应元素的运算操作如+,-,*,/。
举个例子:
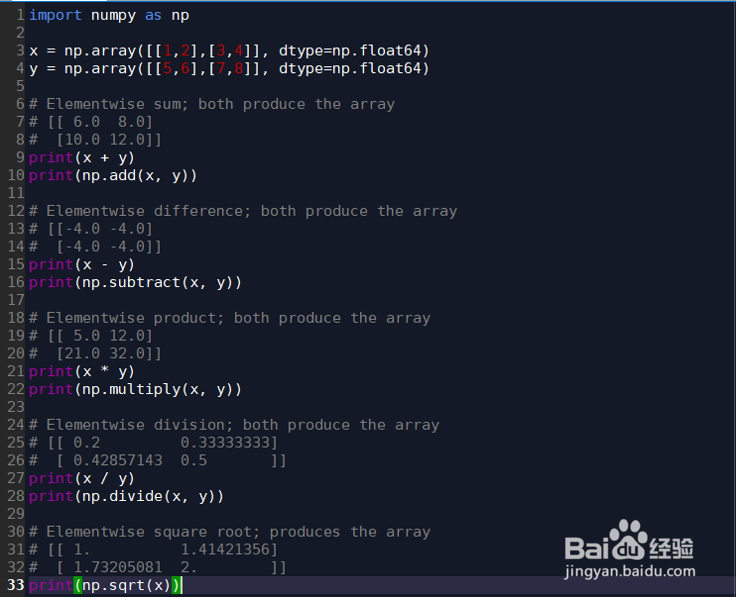
import numpy as np
x = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]], dtype=np.float64)
y = np.array([[5,6],[7,8]], dtype=np.float64)
# Elementwise sum; both produce the array
# [[ 6.0 8.0]
# [10.0 12.0]]
print(x + y)
print(np.add(x, y))
# Elementwise difference; both produce the array
# [[-4.0 -4.0]
# [-4.0 -4.0]]
print(x - y)
print(np.subtract(x, y))
# Elementwise product; both produce the array
# [[ 5.0 12.0]
# [21.0 32.0]]
print(x * y)
print(np.multiply(x, y))
# Elementwise division; both produce the array
# [[ 0.2 0.33333333]
# [ 0.42857143 0.5 ]]
print(x / y)
print(np.divide(x, y))
# Elementwise square root; produces the array
# [[ 1. 1.41421356]
# [ 1.73205081 2. ]]
print(np.sqrt(x))
2、结果显示:
[[ 6. 8.]
[10. 12.]]
[[ 6. 8.]
[10. 12.]]
[[-4. -4.]
[-4. -4.]]
[[-4. -4.]
[-4. -4.]]
[[ 5. 12.]
[21. 32.]]
[[ 5. 12.]
[21. 32.]]
[[0.2 0.33333333]
[0.42857143 0.5 ]]
[[0.2 0.33333333]
[0.42857143 0.5 ]]
[[1. 1.41421356]
[1.73205081 2. ]]

3、numpy使用dot函数实现,向量间的内积,矩阵乘法等运算。
举个例子:
import numpy as np
x = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
y = np.array([[5,6],[7,8]])
v = np.array([9,10])
w = np.array([11, 12])
# Inner product of vectors; both produce 219
print(v.dot(w))
print(np.dot(v, w))
# Matrix / vector product; both produce the rank 1 array [29 67]
print(x.dot(v))
print(np.dot(x, v))
# Matrix / matrix product; both produce the rank 2 array
# [[19 22]
# [43 50]]
print(x.dot(y))
print(np.dot(x, y))

4、运行结果:
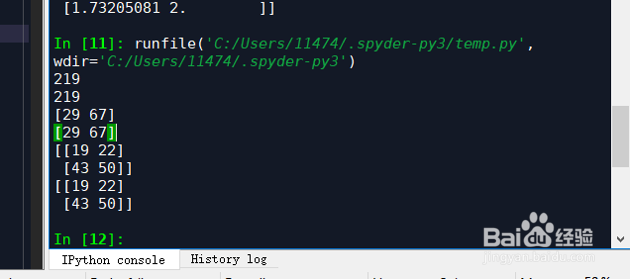
219
219
[29 67]
[29 67]
[[19 22]
[43 50]]
[[19 22]
[43 50]]

5、numpy提供了许多函数对矩阵进行计算。其中最有用的是sum函数。
举个例子:
import numpy as np
x = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
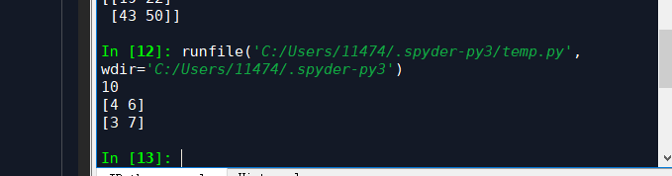
print(np.sum(x)) # Compute sum of all elements; prints "10"
print(np.sum(x, axis=0)) # Compute sum of each column; prints "[4 6]"
print(np.sum(x, axis=1)) # Compute sum of each row; prints "[3 7]"

6、运行结果:
10
[4 6]
[3 7]
7、转置运算:
import numpy as np
x = np.array([[1,2], [3,4]])
print(x) # Prints "[[1 2]
# [3 4]]"
print(x.T) # Prints "[[1 3]
# [2 4]]"
# Note that taking the transpose of a rank 1 array does nothing:
v = np.array([1,2,3])
print(v) # Prints "[1 2 3]"
print(v.T) # Prints "[1 2 3]"
结果:
[[1 2]
[3 4]]
[[1 3]
[2 4]]
[1 2 3]
[1 2 3]