sqlyog代码框架分析
1、 从网上下载SQLyog源代码, 并编译这份源代码, 具体过程见本人的另外一篇经验"sqlyog源代码下载编译教程", 可以在我的经验文章中找到这篇文章, 具体如下图所示:
2、 使用vs2017(假定已经安装支持了MFC)打开SQLyog项目, 在sqlyog-community源代码目录下面有一个build目录, 其中有项目工程文件SQLyogCommunity.sln, 双击可以打开项目, 具体如下图所示:

3、 点击"生成解决方案", 无错误, 输出提示"全部重新生成: 成功 1 个,失败 0 个,跳过 0 个 ", 表明成功编译生成了SQLyog客户端程序, 在"..\sqlyog-community\bin\win32\debug"目录下面生成了一个可执行exe文件SQLyogCommunity.exe, 具体如下图所示:
4、 点击"本地Win...调试器", 启动运行程序, 并让其断点到winmain函数的入口处, 程序启动以后, 首先断点在WinMain函数中, 具体如下图所示:

5、 可以看到在sqlyog项目代码中有WinMain函数, 而Winmain是windows平台下应用程序的入口函数, 具体点说WinMain()函数是Win32程序开始的入口点, 也就表明sqlyog项目是使用Win32 SDK来编码开发实现的。
6、 WinMain函数原型:
int WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance,
HINSTANCE hPreInstance,
LPSTR lpCmdLine,
int nCmdShow );
hInstance ---> 当前实例的句柄
hPrevInstance ---> 前一个实例的句柄
lpCmdLine ---> 命令行参数
nCmdShow ---> 窗体显示形式(最大化、最小化)
7、 在windows下, win32 sdk编写应用程序的一般步骤是:
(1).实现函数WinMain, 也就是根据其原型在源代码中定义它;
(2).创建一个窗口;
(3).进行消息的循环;
(4).编写窗口过程函数。
了解了win32 sdk编程步骤, 下面结合sqlyog项目代码来一步步分析下。
8、 sqlyog项目代码中有一个名为WinMain.cpp的文件, 在这个文件里面实现了函数WinMain, 代码如下:
// Function :
// The main function of the application.
// The start of the software.
wyInt32 WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE hinstance, HINSTANCE hprevinstance,
PSTR cmdline, wyInt32 icmdshow)
{
.......
return msg.wParam;
}
具体如下图:
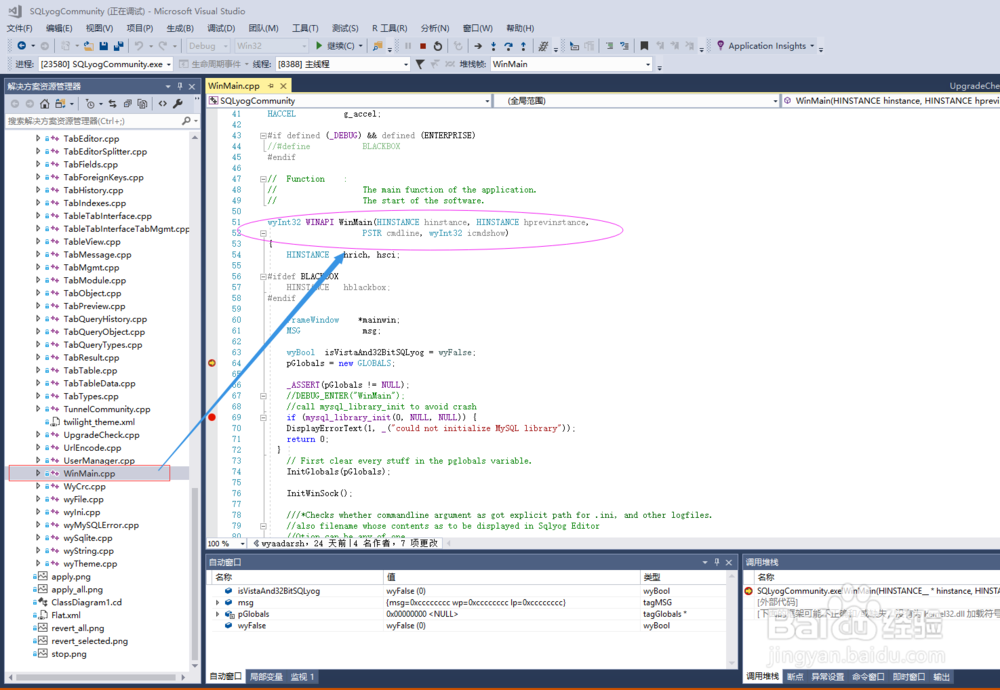
9、 WinMain函数开始是一系列的变量声明, 定义配置与相关的初始化, 具体如下面代码:
HINSTANCE hrich, hsci;
#ifdef BLACKBOX
HINSTANCE hblackbox;
#endif
FrameWindow *mainwin;
MSG msg;
wyBool isVistaAnd32BitSQLyog = wyFalse;
pGlobals = new GLOBALS;
_ASSERT(pGlobals != NULL);
//DEBUG_ENTER("WinMain");
//call mysql_library_init to avoid crash
if (mysql_library_init(0, NULL, NULL)) {
DisplayErrorText(1, _("could not initialize MySQL library"));
return 0;
}
// First clear every stuff in the pglobals variable.
InitGlobals(pGlobals);
InitWinSock();
///*Checks whether commandline argument as got explicit path for .ini, and other logfiles.
//also filename whose contents as to be displayed in Sqlyog Editor
//Otion can be any of one
//i. SQLyogEnt.exe -dir "E:\path" -f "D:\test.sql"
//ii. SQLyogEnt.exe -dir "E:\path" "D:\test.sql"
//iii. SQLyogEnt.exe -f "D:\test.sql" -dir "E:\path" -f
//-dir stands for explicit path for .ini, tags, logs, favourites , etc
//-f stands for file to be oponed in editor
//*/
//Gets the Attributes passed through command line(-f, -dir)
if(pGlobals->m_configdirpath.GetLength())
//unsigned long len=0;
// if(len=pGlobals->m_configdirpath.GetLength())
pGlobals->m_configdirpath.Clear();
if(GetConfigDetails(cmdline) == wyFalse)
return 0;
CreateInitFile();
#ifndef _WIN64
OSVERSIONINFOEX osvi;
osvi.dwOSVersionInfoSize = sizeof(OSVERSIONINFOEX);
//get the OS version and set the display style accordingly
if (GetVersionEx((OSVERSIONINFO*)&osvi)) {
if (osvi.dwMajorVersion == 6 && osvi.dwMinorVersion == 0 && osvi.wProductType == VER_NT_WORKSTATION)
isVistaAnd32BitSQLyog = wyTrue;
}
#endif
#ifdef _DEBUG
HANDLE hlogfile = NULL;
hlogfile = CreateFile(L"SQLyog_debug_log.txt", GENERIC_WRITE, FILE_SHARE_WRITE,
NULL, CREATE_ALWAYS, FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL, NULL);
#else
//Initialize the Path for .INI & .dmp files
CreateInitFile();
if (isVistaAnd32BitSQLyog == wyFalse) {
MiniDump dumpcrash;
if (IsCrashDumpSupported() == wyTrue)
dumpcrash.InitDumpDetails(pGlobals->m_configdirpath.GetString());
}
#endif
_CrtSetReportMode(_CRT_WARN, _CRTDBG_MODE_FILE | _CRTDBG_MODE_WNDW);
_CrtSetReportFile(_CRT_WARN, hlogfile);
_CrtSetReportMode(_CRT_ERROR, _CRTDBG_MODE_FILE | _CRTDBG_MODE_WNDW);
_CrtSetReportFile(_CRT_ERROR, hlogfile);
_CrtSetReportMode(_CRT_ASSERT, _CRTDBG_MODE_FILE | _CRTDBG_MODE_WNDW);
_CrtSetReportFile(_CRT_ASSERT, hlogfile);
_CrtSetReportMode(_CRT_WARN, _CRTDBG_MODE_FILE );
_CrtSetReportFile(_CRT_WARN, hlogfile);
_CrtSetReportMode(_CRT_ERROR, _CRTDBG_MODE_FILE );
_CrtSetReportFile(_CRT_ERROR, hlogfile);
_CrtSetReportMode(_CRT_ASSERT, _CRTDBG_MODE_FILE );
_CrtSetReportFile(_CRT_ASSERT, hlogfile);
_CrtSetDbgFlag ( _CRTDBG_ALLOC_MEM_DF | _CRTDBG_LEAK_CHECK_DF );
VERIFY(hsci = ::LoadLibrary(L"SciLexer.dll"));
if(!hsci)
{
DisplayErrorText(GetLastError(), _("Error loading SciLexer.dll"));
VERIFY(FreeLibrary(hsci));
return 0;
}
pGlobals->m_statusbarsections = STATUS_BAR_SECTIONS;
/* register scintilla */
//Scintilla_RegisterClasses(NULL);
#ifndef VC6
/* startup gdiplus...this is required to display image in BLOB window */
ULONG_PTR gditoken;
Gdiplus::GdiplusStartupInput startupinput;
Gdiplus::GdiplusStartup(&gditoken, &startupinput, NULL);
#endif
pGlobals->m_hinstance = hinstance;
VERIFY(hrich = ::LoadLibrary(L"Riched20.dll"));
#ifdef BLACKBOX
VERIFY(hblackbox = ::LoadLibrary(L"BlackBox.dll"));
#endif
/* check for library problems */
if(!hrich)
{
DisplayErrorText(GetLastError(), _("Error loading riched20.dll"));
VERIFY(FreeLibrary(hsci));
return 0;
}
为整个sqlyog项目的运行做初始化准备工作。
10、 初始化准备工作完成以后, 使用以下代码来创建sqlyog软件相关的窗口:
pGlobals->m_findreplace = wyFalse;
CreateCustomTabIconList();
// Initialize the common controls.
InitCustomControls();
CollectCurrentWindowsVersion();
pGlobals->m_modulenamelength = GetModuleNameLength();
wyTheme::SubclassControls();
if(!pGlobals->m_modulenamelength)
{
DisplayErrorText(GetLastError(), _("GetModuleFileName length failed!"));
return 0;
}
SetLanguage(NULL, wyTrue);
wyTheme::Init();
// Create the mainwindow.
mainwin = new FrameWindow(pGlobals->m_hinstance);
类FrameWindow是sqlyog客户端的主界面窗口对应的类函数, 也就是整个应用程序的主窗口, 定义实现的文件在FrameWindow.h和FrameWindow.cpp, 这样子就有了程序的主框架窗口了, ui界面层的最大部分我们已经知道是如何生成的了。
11、 sqlyog客户端主界面确立以后, 接下来我们就需要事先消息循环了, 整个循环主要是来处理消息的,代码如下所示:
// The main loop for messages.
while(GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0))
{
if(pGlobals->m_pcmainwin->m_finddlg)
{
if((pGlobals->m_pcmainwin->m_finddlg && IsWindowVisible(pGlobals->m_pcmainwin->m_finddlg)&&
IsDialogMessage(pGlobals->m_pcmainwin->m_finddlg, &msg)))
{
pGlobals->m_findreplace = wyTrue;
continue;
}
}
if(!TranslateMDISysAccel(pGlobals->m_hwndclient, &msg))
{
if(!(TranslateAccelerator(mainwin->GetHwnd(), g_accel, &msg)))
{
/// code to catch Accel(short-cuts for Save & Revert) key-press on Create/Alter table tabbed interface
if(pGlobals->m_pcmainwin->m_htabinterface && IsDialogMessage(pGlobals->m_pcmainwin->m_htabinterface, &msg))
{
continue;
}
if(pGlobals->m_pcmainwin->m_hwndtooltip && msg.message == WM_LBUTTONDOWN)
{
FrameWindow::ShowQueryExecToolTip(wyFalse);
}
pGlobals->m_findreplace = wyFalse;
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
}
}
上面代码开启了消息循环。
Windows操作系统为每一个正在运行的应用程序保持有一个消息队列。
当有事件发生后, Windows并不是将这个激发事件直接送给应用程序,
而是先将其翻译成一个Windows消息,
然后再把这个消息加入到这个应用程序的消息队列中去。
应用程序需要通过消息循环来接收这些消息。
即Windows 中有一个系统消息队列, 对于每一个正在执行的Windows应用程序, 系统为其建立一个"消息队列", 即应用程序队列,用来存放该程序可能创建的各种窗口的消息。
应用程序中含有一段称作"消息循环"的代码,
用来从消息队列中检索这些消息并把它们分发到相应的窗口函数中。
Windows是以消息驱动的操作系统, Windows 消息提供了应用程序与Windows系统之间进行通讯的手段。
Windows应用程序是基于消息的程序设计模式, 使用事件驱动编程模型,
分为消息概述、消息结构、消息类型。
消息循环代码是应用程序中主函数WinMain ( )中类似如下的程序段:
while(GetMessage(&msg,NULL,0,0))
{
TranslateMessage(&msg); //从消息队列中取得消息
DispatchMessage(&msg); //检索并生成字符消息WM_CHAR
//将消息发送给相应的窗口函数
}
由此可见, 所谓"消息循环", 实际是程序循环。
可以看到sqlyog客户端应用程序的消息循环就是在WinMain.cpp中实现的。
12、 由于Windows 应用程序创建的每个窗口都在系统核心注册一个相应的窗口函数, 窗口函数程序代码形式上是一个巨大的switch 语句, 用以处理由消息循环发送到该窗口的消息, 窗口函数由Windows 采用消息驱动的形式直接调用,
而不是由应用程序显示调用的, 窗口函数处理完消息后又将控制权
返回给Windows。
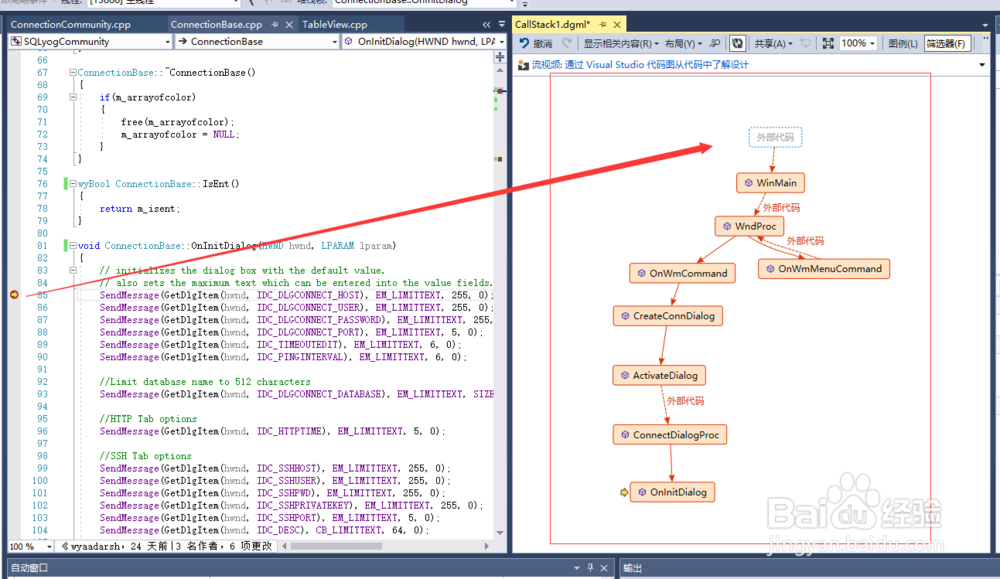
也就是说sqlyog客户端应用程序中的每个窗口都会注册一个相应的窗口函数, 而每个窗口都对应有一个头文件和一个cpp文件, 举例如"Connect to MySQL Host"这个窗口(File--->New Connection...), 可以看到整个过程的调用代码堆栈图下图所示, 可以看到最顶层的是FrameWindow::WndProc()函数,
// The window procedure for MainWindow.
// It creates all its child window in WM_CREATE message.
LRESULT CALLBACK FrameWindow::WndProc(HWND hwnd, UINT message, WPARAM wparam, LPARAM lparam)
{
........
}
整个函数窗口过程函数在WM_CREATE消息响应时候创建了所有子窗口,
case WM_CREATE:
pcmainwin->OnCreate();
return 0;
函数代码如下:
void FrameWindow::OnCreate()
{
// CreateToolBarWindow();
CreateStatusBarWindow();
CreateMDIWindow();
m_findmsg = RegisterWindowMessage(FINDMSGSTRING);
CheckForAutoKeywords();
ConvertIniFileToUtf8();
MigrateFiles();
//MigratePersonalFolderToFavorites();
return;
}
在这里创建了主界面窗口的子窗口, 每个子窗口都有一个窗口过程函数来处理各自的消息, 到此sqlyog客户端整个主体框架分析完毕。