OpenCV函数:提取轮廓相关函数使用方法
1、findContours()查找轮廓:
void findContours (
InputOutputArray image,//输入图像,必须是8位单通道二值图像
OutputArrayOfArrays contours,//检测到的轮廓,每个轮廓被表示成一个point向量
OutputArray hierarchy,//可选的输出向量,包含图像的拓扑信息。其中元素的个数和检测到的轮廓的数量相等
int mode,//说明需要的轮廓类型和希望的返回值方式
int method,//轮廓近似方法
Point offset = Point()
)
参数mode:
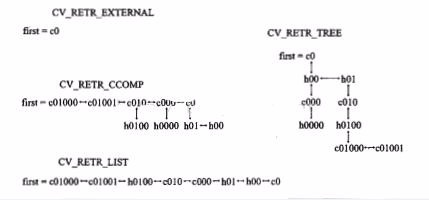
①mode的值决定把找到的轮廓如何挂到轮廓树节点变量(h_prev, h_next, v_prev, v_next)上,拓扑结构图如下;
②每种情况下,结构都可以看成是被横向连接(h_prev, h_next)联系和被纵向连接(v_prev, v_next)不同层次。
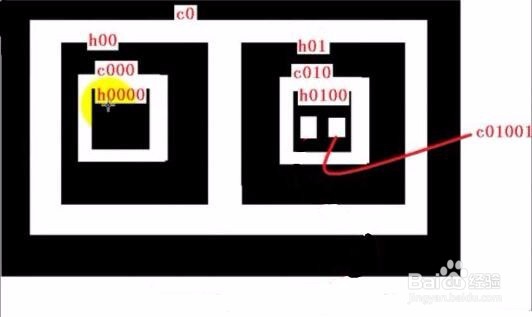
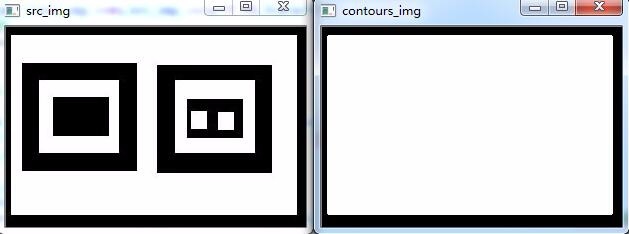
③CV_RETR_EXTERNAL:只检测出最外轮廓即c0;
CV_RETR_LIST:检测出所有的轮廓并将他们保存到表(list)中;
CV_RETR_COMP:检测出所有的轮廓并将他们组织成双层的结构,第一层是外部轮廓边界,第二层边界是孔的边界;
CV_RETR_TREE:检测出所有轮廓并且重新建立网状的轮廓结构;
④参数method:
CV_CHAIN_CODE:用freeman链码输出轮廓,其他方法输出多边形(顶点的序列);
CV_CHAIN_APPROX_NONE:将链码编码中的所有点转换为点;
CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE:压缩水平,垂直或斜的部分,只保存最后一个点;
CV_CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_L1,CV_CHAIN_QPPROX_TC89_KCOS:使用Teh-Chin链逼近算法中的一个。
CV_LINK_RUNS:与上述的算法完全不同,连接所有的水平层次的轮廓。
【注】:findContours()查找时,这个图像会被直接涂改,因此如果是以后有用的图像,应该复制之后再进行查找;
2、drawContours()绘制轮廓:
void drawContours(
InputOutputArray image,//要绘制轮廓的图像
InputArrayOfArrays contours,//所有输入的轮廓,每个轮廓被保存成一个point向量
int contourIdx,//指定要绘制轮廓的编号,如果是负数,则绘制所有的轮廓
const Scalar& color,//绘制轮廓所用的颜色
int thickness = 1, //绘制轮廓的线的粗细,如果是负数,则轮廓内部被填充
int lineType = 8, /绘制轮廓线的连通性
InputArray hierarchy = noArray(),//关于层级的可选参数,只有绘制部分轮廓时才会用到
int maxLevel = INT_MAX,//绘制轮廓的最高级别,这个参数只有hierarchy有效的时候才有效
Point offset = Point()
)
【注】:
①maxLevel=0,绘制与输入轮廓属于同一等级的所有轮廓即输入轮廓和与其相邻的轮廓
maxLevel=1, 绘制与输入轮廓同一等级的所有轮廓与其子节点。
maxLevel=2,绘制与输入轮廓同一等级的所有轮廓与其子节点以及子节点的子节点

3、轮廓填充:
步骤:
a) 依次遍历轮廓点,将点绘制到img上;
b) 使用floodFill以及一个种子点进行填充;
两种方法:自己编写程序;使用drawContours()函数;
void drawMaxAreaLine(Mat& dst, vector<Point> maxAreaPoints)
{
int step = dst.step;
auto data = dst.data;
for (int i = 0; i < maxAreaPoints.size(); ++i)
{
*(data + maxAreaPoints[i].x + maxAreaPoints[i].y * step) = 255;
}
}
//孔洞填充算法
void fillHole(Mat src_Bw, Mat &dst_Bw)
{
Size m_Size = src_Bw.size();
Mat Temp=Mat::zeros(m_Size.height+10,m_Size.width+10,src_Bw.type());
src_Bw.copyTo(Temp(Range(5, m_Size.height + 5), Range(5, m_Size.width + 5)));
floodFill(Temp, Point(0, 0), Scalar(255));
Mat cutImg;
Temp(Range(5, m_Size.height + 5), Range(5, m_Size.width + 5)).copyTo(cutImg);
dst_Bw = src_Bw | (~cutImg);
}
【注】:这里常会碰到种子点不好选取的问题,因为有时候所选择的种子点不能保证对所有轮廓都适用。也就是查找一个在轮廓内的点是存在一定难度的。
使用drawContours()就会很方便:
vector<vector<Point> > contours;
contours.push_back(currentFrameEdge);
Mat savedGrayMat = Mat::zeros(RectData[0].rows, RectData[0].cols, CV_8UC1);
//drawMaxAreaLine(savedGrayMat, currentFrameEdge);
//floodFill(savedGrayMat, Point(currentFrameEdge[0].x + 2, currentFrameEdge[0].y + 2), 255);
drawContours(savedGrayMat, contours, 0, Scalar(255), CV_FILLED);
imshow("savedGrayMat", savedGrayMat);
waitKey();
4、计算轮廓的面积和周长:
①计算轮廓面积:
double contourArea(InputArray contour, bool oriented=false )
InputArray contour:输入的点,一般是图像的轮廓点;
bool oriented=false: 表示某一个方向上轮廓的的面积值,顺时针或者逆时针,一般选择默认false;
②计算轮廓边长:
double arcLength(InputArray curve, bool closed)
InputArray curve:表示图像的轮廓;
bool closed:表示轮廓是否封闭的;
【注】:
①contourArea计算整个或部分轮廓的面积;
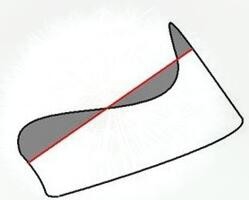
在计算部分轮廓的情况时,由轮廓弧线和连接两端点的弦围成的区域总面积被计算,如图;
②轮廓的位置将影响区域面积的符号,因此函数范围的有可能是负值。可以在运行时使用fabs()来得到面积的绝对值;

5、提取轮廓凸包,矩形,最小外接矩形,外接圆
①convexhull():函数提取轮廓的凸包:
格式:
void convexhul(InputArray points,
OutputArray hull,
bool clockwise=false,
bool returnPoints=true)
参数:
第一个参数:要求凸包的点集
第二个参数:输出的凸包点,可以为vector,此时返回的是凸包点在原轮廓点集中的索引,也可以为vector,此时存放的是凸包点的位置
第三个参数:一个bool变量,表示求得的凸包是顺时针方向还是逆时针方向,true是顺时针方向;
第四个参数,第二个参数的返回类型是vector还是vector,可以忽略;
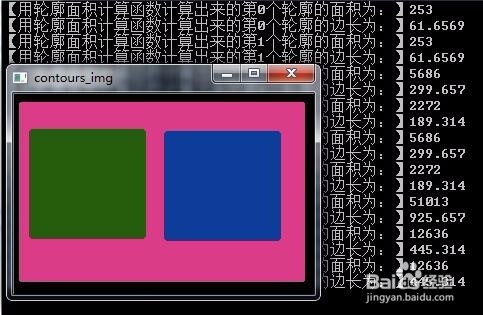
②boundingRect():计算轮廓外包矩形,矩形是与图像上下边界平行的;
格式:
Rect boundingRect(InputArray points);
输入:二维点集,点的序列或向量 (Mat)
返回:Rect
//寻找外包矩阵
Rect maxRect = boundingRect(contours[m_count]);
//绘制外包矩阵
rectangle(contours_img_1, maxRect, Scalar(0, 255, 0));
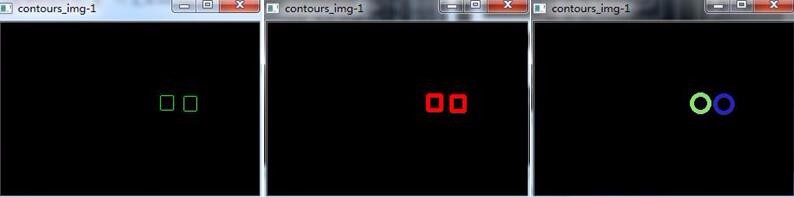
③minAreaRect():提取轮廓的最小外包矩形;
主要求包含点集最小面积的矩形,这个矩形是可以有偏转角度的,可以与图像的边界不平行;
格式:
RotatedRect minAreaRect(InputArray points)
输入:二维点集,点的序列或向量 (Mat)
返回:RotatedRect
④minEnclosingcircle():提取轮廓的最小外包圆;
格式:
void minEnclosingcircle(InputArray points,Point2f& center,float& radius)
输入:
二维点集:点的序列vector< point >或向量 (Mat) ,
圆心坐标;
半径;

6、示例:
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include "opencv2/contrib/contrib.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
void KmeansFun();
void fillHole(Mat src_Bw, Mat &dst_Bw);
int main()
{
Mat src_img = imread("data\\00.jpg",1);
Mat src_img_1(src_img.rows,src_img.cols,CV_8UC1,Scalar(0));
cvtColor(src_img, src_img_1, CV_BGR2GRAY);
GaussianBlur(src_img_1, src_img_1, Size(3, 3), 3, 3);
Mat threshold_img(src_img.rows,src_img.cols,CV_8UC1,Scalar(0));
threshold(src_img_1, threshold_img, 0, 255, THRESH_OTSU);
imshow("1",threshold_img);
vector< vector<Point> > contours;
vector<Vec4i> hierarchy;
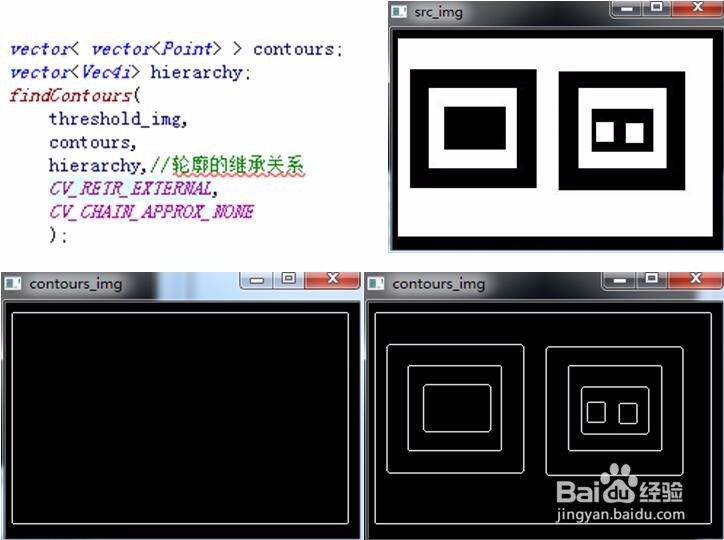
findContours(
threshold_img,
contours,
hierarchy,//轮廓的继承关系
CV_RETR_CCOMP,
CV_CHAIN_APPROX_NONE
);
Mat contours_img(src_img.rows,src_img.cols,CV_8U,Scalar(0));
if(!contours.empty() && !hierarchy.empty())
{
int idx = 0;
for( ; idx >= 0; idx = hierarchy[idx][0] )
{
Scalar color(255,255,255);
//Scalar color( (rand()&255), (rand()&255), (rand()&255) );//随机生成颜色
drawContours( contours_img, contours, idx, color, 1, 8, hierarchy );
}
}
imshow("contours_img",contours_img);
int m_count = 0;
Mat contours_img_1(src_img.rows,src_img.cols,CV_8UC3,Scalar(0));
if(!contours.empty() && !hierarchy.empty()) //计算轮廓的面积
{
for (int i = 0; i < (int)contours.size(); i++)
{
double g_dConArea = abs(contourArea(contours[i], false));
double g_dConLength = arcLength(contours[i],true);
cout << "【用轮廓面积计算函数计算出来的第" << i << "个轮廓的面积为:】" << g_dConArea << endl;
cout << "【用轮廓面积计算函数计算出来的第" << i << "个轮廓的边长为:】" << g_dConLength << endl;
if (g_dConArea >= 10 && g_dConArea < 300)
{
m_count = i;
//Scalar color( (rand()&255), (rand()&255), (rand()&255) );//随机生成颜色
//drawContours(contours_img_1, contours, m_count, color, CV_FILLED, 8, hierarchy );//对轮廓内部着色
//计算凸包
//vector<int> hull;
//convexHull(Mat(contours[m_count]), hull, true);
////绘制凸包
//int hull_count = (int)hull.size();
//Point pt0 = contours[m_count][hull[hull_count - 1]];
//for (int i = 0;i < hull_count;i++)
//{
// Point pt = contours[m_count][hull[i]];
// line(contours_img_1, pt0, pt, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1,8);
// pt0 = pt;
//}
////寻找外包矩阵
//Rect maxRect = boundingRect(contours[m_count]);
////绘制外包矩阵
//rectangle(contours_img_1, maxRect, Scalar(0, 255, 0));
////寻找最小外包矩形
//RotatedRect minRect = minAreaRect(contours[m_count]);
//Point2f fourPoint2f[4];
////将minRect的四个顶点坐标值放到fourPoint的数组中
//minRect.points(fourPoint2f);
////根据得到的四个点的坐标 绘制矩形
//for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
//{
// line(contours_img_1, fourPoint2f[i], fourPoint2f[i + 1], Scalar(0,0,255), 3);
//}
//line(contours_img_1, fourPoint2f[0], fourPoint2f[3], Scalar(0, 0, 255), 3);
//在生成的那些随机点中寻找最小包围圆形
Point2f center; //圆心
float radius; //半径
minEnclosingCircle(contours[m_count], center, radius);
//根据得到的圆形和半径 绘制圆形
circle(contours_img_1, static_cast<Point>(center), (int)radius, Scalar( (rand()&255), (rand()&255), (rand()&255) ), 3);
}
}
}
imshow("src_img",src_img);
imshow("contours_img-1",contours_img_1);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
