C++标准库:sstream类型转换
1、<sstream> VS <stdio.h>:
对于<stdio.h>风格的类型转换,学习基于<sstream>的类型转换是有必要的。
<stdio.h>中,sprintf()函数将变量从int类型转换到string类型。
首先,需要确保目标缓冲区有足够大空间以容纳转换完的字符串;
其次,必须使用正确的格式化符,否则会导致非预知的后果。
如:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int i=10;
char name[30];
sprintf(name,"pic\\left%02d.png",i);
cout<<name<<endl;
return 0;
}
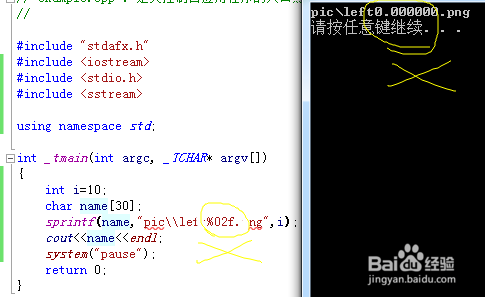
如果使用了不正确的格式化符就会使结果错误:
int i=10;
char name[30];
sprintf(name,”pic\\left%02f.png”,i);//%02f
cout<<name<<endl;

2、<sstream>
<sstream>是C++新标准发行的,
<sstream>库定义了三种类:
istringstream流输入操作、ostringstream流输出操作和stringstream流输入输出操作。
<sstream>优点:
使用string对象代替char *,可以避免缓冲区溢出的危害;
输入变量类型和输出对象类型被自动推导出来,即使使用了不正确的格式化符也没影响,更加安全;
<sstream>流程:
编译器首先在编译器确定输入和输出变量的类型,判读需要进行哪些变换;然后自动选择转换类型,转换结果保存在stringstream对象的内部缓存中,且不必担心缓冲区溢出,程序会自动为这些对象分配存储空间。
例:
string到int的类型转换:
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
string result="250";
int n=0;
stringstream stream;
stream << result;
stream >> n;//n等̨¨于®¨²250
cout<<n<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

3、定义模板函数string
定义一个任意类型转换到特定目标类型的函数模板。
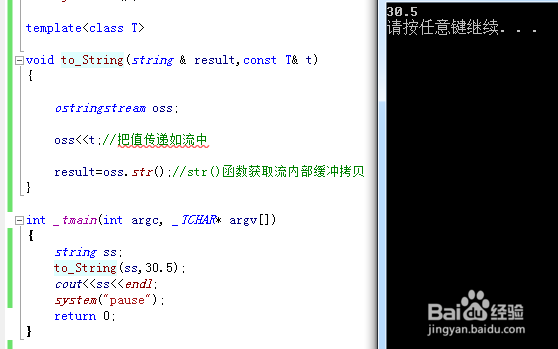
例:创建to_string()函数,将int、long、double等转换成string;
void to_String(string & result,const T& t)
{
ostringstream oss;
oss<<t;//
result=oss.str();
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
string ss;
to_String(ss,30.5);
//to_String(ss,1234);
//to_String(ss,true);
cout<<ss<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
4、定义模板函数convert
定义含有两个参数任意类型转换到特定目标类型的函数模板convert。
例:将in_value值转换成out_type类型。
template<class out_type,class in_value>
out_type convert(const in_value & t)
{
stringstream stream;
stream<<t;//向¨°流¢¡Â中D传ä?值¦Ì
out_type result;//这a里¤?存ä?储ä¡é转Áa换?结¨¢果?
stream>>result;//向¨°result中D写¡ä入¨?值¦Ì
return result;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
double d;
string salary;
string ss="12.56";
d=convert<double>(ss);//string->doule
salary=convert<string>(9000.0);//double->string
cout<<d<<"\n"<<salary<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

5、重复使用同一个stringstream对象
【注】:多次转换中使用同一个stringstream对象,在每次转换前使用clear()函数清空缓冲区。
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
stringstream stream;
int first, second;
stream << "456"; //插入字符串
stream >> first; //转换成int
cout << first << endl;
/*此时stream已经是eofbit状态了 所以接下来需要进行clear才能继续往stream写入数据*/
stream.clear(); //在进行多次转换前,必须清除stream
stream << true; //插入bool值
stream >> second; //提取出int
//如果stream中的字符串没有全部读取完,可以用str("")来清空,所以根据不同的情况使用clear和str。
cout << second << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

