Java实现链表反转的一个示例
1、这两天在研究JDK1.6 HashMap的源码,看着链表比较有趣,就参照HashMap resize时的transfer方法写了一个链表翻转的Demo
先看看输出的效果:
entry:E1-key=E1-value
entry.next:E2-key=E2-value
===================华丽的分隔线===================
entry:E2-key=E2-value
entry.next:E1-key=E1-value

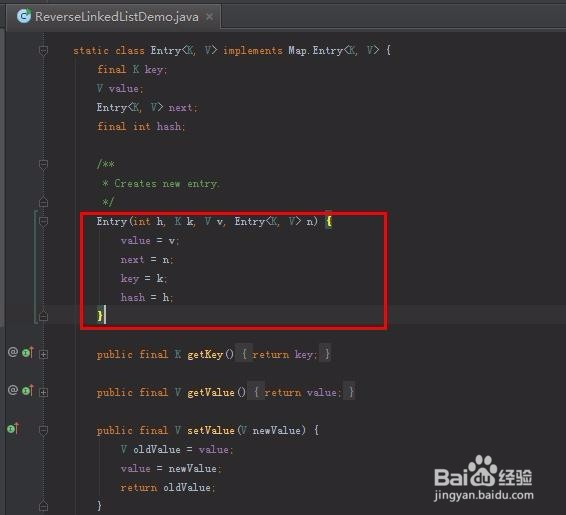
2、来看看对Node节点class的定义
此处继承了Map.Entry的结构
static class Entry<K, V> implements Map.Entry<K, V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K, V> next;
final int hash;
/**
* Creates new entry.
*/
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K, V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
public final K getKey() {
return key;
}
public final V getValue() {
return value;
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry) o;
Object k1 = getKey();
Object k2 = e.getKey();
if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) {
Object v1 = getValue();
Object v2 = e.getValue();
if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2)))
return true;
}
return false;
} public final int hashCode() {
return (key == null ? 0 : key.hashCode()) ^ (value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
} public final String toString() {
return getKey() + "=" + getValue();
}
/**
* This method is invoked whenever the value in an entry is
* overwritten by an invocation of put(k,v) for a key k that's already
* in the HashMap.
*/
void recordAccess(HashMap<K, V> m) {
}
/**
* This method is invoked whenever the entry is
* removed from the table.
*/
void recordRemoval(HashMap<K, V> m) {
}
}
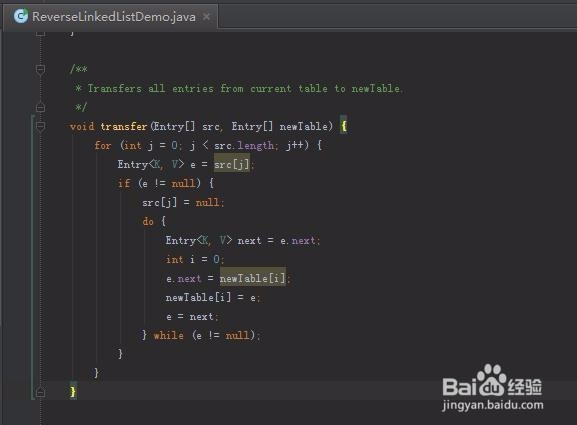
3、反转链表的代码:
void transfer(Entry[] src, Entry[] newTable) {
for (int j = 0; j < src.length; j++) {
Entry<K, V> e = src[j];
if (e != null) {
src[j] = null;
do {
Entry<K, V> next = e.next;
int i = 0;
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
} while (e != null);
}
}
}
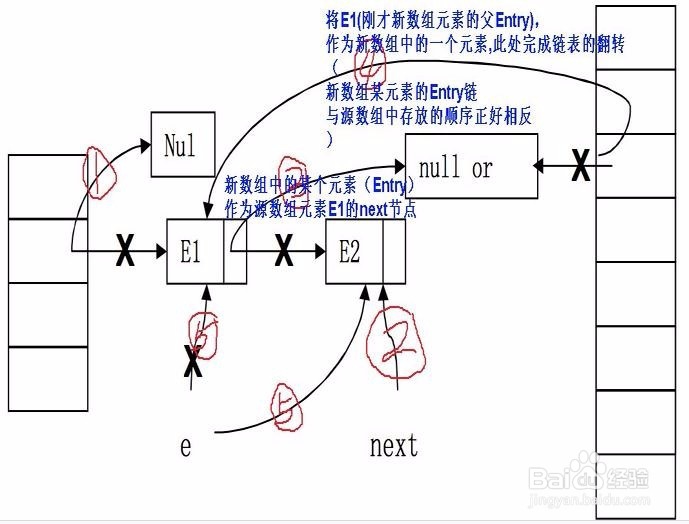
4、解析一下反转链表的逻辑
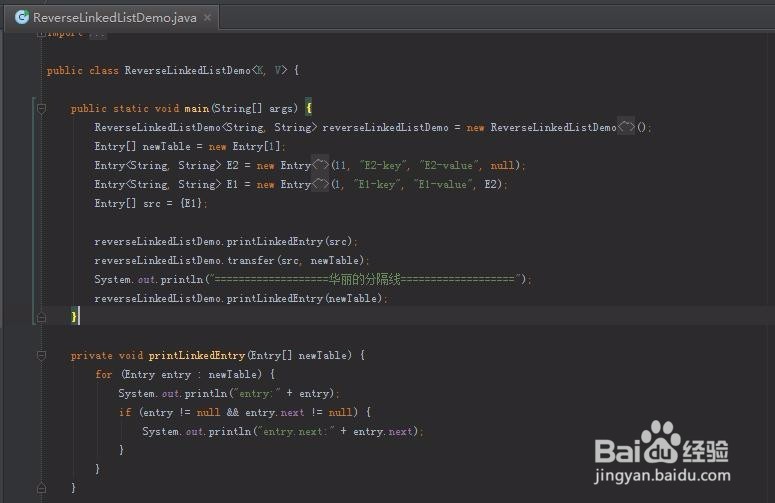
5、看看main方法
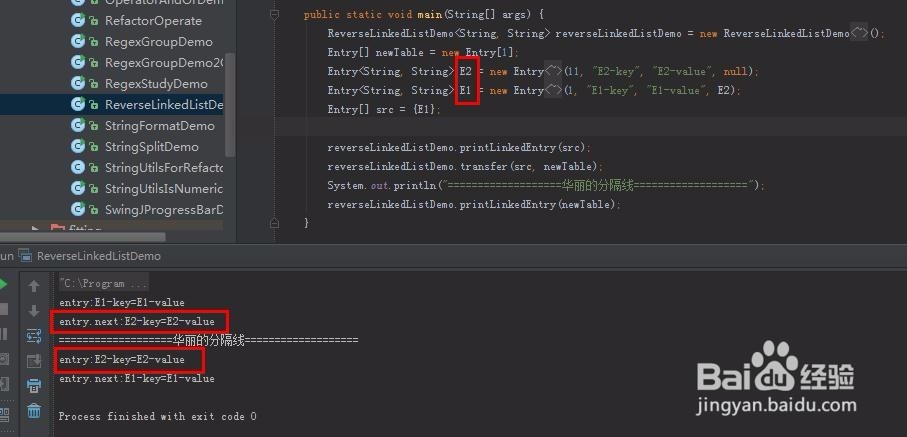
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReverseLinkedListDemo<String, String> reverseLinkedListDemo = new ReverseLinkedListDemo<String, String>();
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[1];
Entry<String, String> E2 = new Entry<String, String>(11, "E2-key", "E2-value", null);
Entry<String, String> E1 = new Entry<String, String>(1, "E1-key", "E1-value", E2);
Entry[] src = {E1};
reverseLinkedListDemo.printLinkedEntry(src);
reverseLinkedListDemo.transfer(src, newTable);
System.out.println("===================华丽的分隔线===================");
reverseLinkedListDemo.printLinkedEntry(newTable);
}
6、执行下,看看结果
entry:E1-key=E1-value
entry.next:E2-key=E2-value
===================华丽的分隔线===================
entry:E2-key=E2-value
entry.next:E1-key=E1-value
7、粘一下完整的代码:
Code:
package chapter4;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ReverseLinkedListDemo<K, V> {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReverseLinkedListDemo<String, String> reverseLinkedListDemo = new ReverseLinkedListDemo<String, String>();
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[1];
Entry<String, String> E2 = new Entry<String, String>(11, "E2-key", "E2-value", null);
Entry<String, String> E1 = new Entry<String, String>(1, "E1-key", "E1-value", E2);
Entry[] src = {E1};
reverseLinkedListDemo.printLinkedEntry(src);
reverseLinkedListDemo.transfer(src, newTable);
System.out.println("===================华丽的分隔线===================");
reverseLinkedListDemo.printLinkedEntry(newTable);
} private void printLinkedEntry(Entry[] newTable) {
for (Entry entry : newTable) {
System.out.println("entry:" + entry);
if (entry != null && entry.next != null) {
System.out.println("entry.next:" + entry.next);
}
}
}
/**
* Transfers all entries from current table to newTable.
*/
void transfer(Entry[] src, Entry[] newTable) {
for (int j = 0; j < src.length; j++) {
Entry<K, V> e = src[j];
if (e != null) {
src[j] = null;
do {
Entry<K, V> next = e.next;
int i = 0;
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
} while (e != null);
}
}
}
static class Entry<K, V> implements Map.Entry<K, V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K, V> next;
final int hash;
/**
* Creates new entry.
*/
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K, V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
} public final K getKey() {
return key;
}
public final V getValue() {
return value;
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry) o;
Object k1 = getKey();
Object k2 = e.getKey();
if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) {
Object v1 = getValue();
Object v2 = e.getValue();
if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2)))
return true;
}
return false;
} public final int hashCode() {
return (key == null ? 0 : key.hashCode()) ^ (value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
} public final String toString() {
return getKey() + "=" + getValue();
} /**
* This method is invoked whenever the value in an entry is
* overwritten by an invocation of put(k,v) for a key k that's already
* in the HashMap.
*/
void recordAccess(HashMap<K, V> m) {
}
/**
* This method is invoked whenever the entry is
* removed from the table.
*/
void recordRemoval(HashMap<K, V> m) {
}
}
}