java单例模式怎么做
1、第一种:懒汉模式。
特点:到需要用的时候才实例化,实现了懒加载
线程不安全
代码如下:
/** * 懒汉模式 */public class SingLetonLazy { private static SingLetonLazy instance; private SingLetonLazy(){ } public static SingLetonLazy getInstance(){ if(instance==null){ instance=new SingLetonLazy(); } return instance; }}

2、第二种:全局访问点加同步的懒汉模式。
由于synchronized是锁方法, 当两个线程都要进入getsingle()时, 只有一个能进入, 并创建出实例, 然后另外一个进入后, 判断 s不为null, 然后直接得到s。 这种做法是没有错误的. 但是由于线程都需要通过getsingle()来获取对象, 所以getsingle()调用频率很高, 所以线程被锁的频率也很高, 所以这种做法效率低。简言之,不管对象有没有被创建,其余线程都只能等待这个方法的锁。
线程安全。
/** * 懒汉模式 */public class SingLetonLazy { private static SingLetonLazy instance = null; private SingLetonLazy(){} public static synchronized SingLetonLazy getInstance(){ if(null == instance){ instance = new Singleton(); } return instance; }}

3、第三种:双重检查锁定懒汉模式。
这种在效率上比第二种高一些,减少了第二种加锁的的范围。
线程安全。
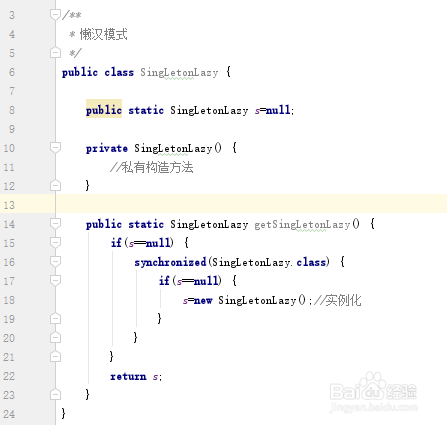
/** * 懒汉模式 */public class SingLetonLazy { public static SingLetonLazy s=null; private SingLetonLazy() { //私有构造方法 } public static SingLetonLazy getSingLetonLazy() { if(s==null) { synchronized(SingLetonLazy.class) { if(s==null) { s=new SingLetonLazy();//实例化 } } } return s; }}
4、第四种:饿汉模式。
特点:在程序启动,类加载的时候就初始化
线程安全
代码如下:
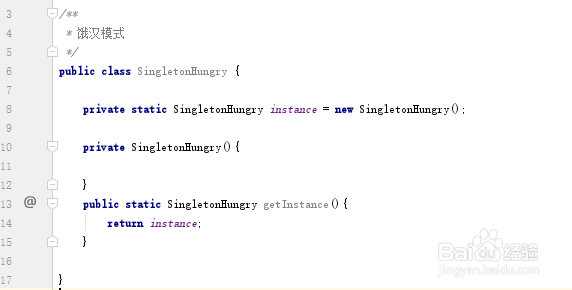
/** * 饿汉模式 */public class SingletonHungry { private static SingletonHungry instance = new SingletonHungry(); private SingletonHungry(){ } public static SingletonHungry getInstance(){ return instance; }}
5、第五种:静态内部类实现懒汉模式。
特点:借助内部类的静态语句块实现
线程安全。
/*** 懒汉模式*/public class SingLetonLazy { // 静态内部类 private static class NestClass { private static SingLetonLazy instance; static { instance = new SingLetonLazy(); } } // 不能直接new private SingLetonLazy() { } public static SingLetonLazy getSingLetonLazy() { return NestClass.instance; }}

6、第六种:枚举(优先选择这一种方式) 。
JDK 版本:JDK1.5 起
是否 Lazy 初始化:否
是否多线程安全:是
实现难度:易
描述:这种实现方式还没有被广泛采用,但这是实现单例模式的最佳方法。它更简洁,自动支持序列化机制,绝对防止多次实例化。这种方式是 Effective Java 作者 Josh Bloch 提倡的方式,它不仅能避免多线程同步问题,而且还自动支持序列化机制,防止反序列化重新创建新的对象,绝对防止多次实例化。不过,由于 JDK1.5 之后才加入 enum 特性,用这种方式写不免让人感觉生疏,在实际工作中,也很少用。不能通过 reflection attack 来调用私有构造方法。
代码如下:
public enum EnumSingleton {
INSTANCE{
@Override
protected void work() {
System.out.println("你好,是我!");
}
};
//单例需要进行操作(也可以不写成抽象方法)
protected abstract void work();
}

7、第七步:测试。
1、首先编写代码实现多线程
2、将累计足够的线程然后同时触发创建类请求
3、对比请求的类是否是同一个。