java jdk1.8新特性Lambda表达式
1、初识lambda表达式:
package com.sgg.lambda;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import org.junit.Test;
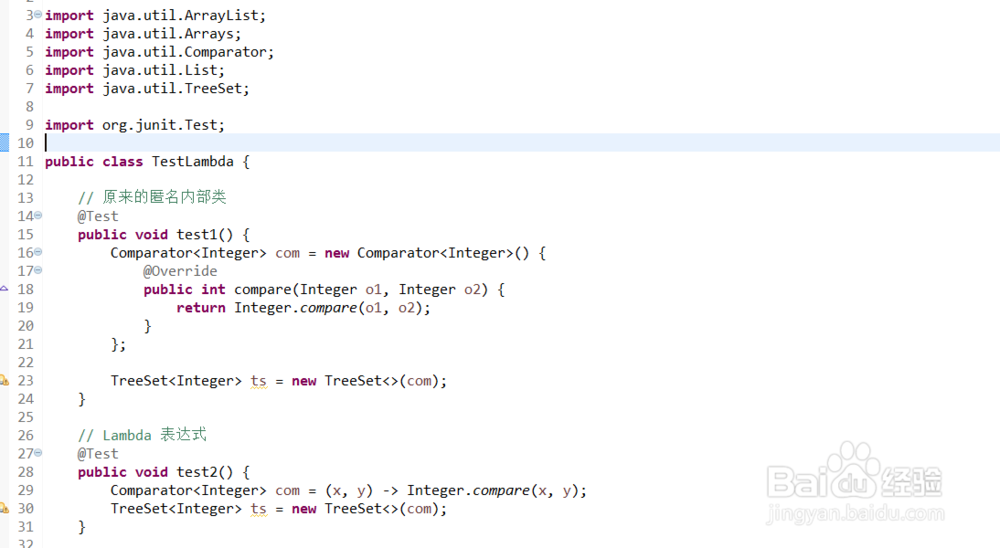
public class TestLambda {
// 原来的匿名内部类
@Test
public void test1() {
Comparator<Integer> com = new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return Integer.compare(o1, o2);
}
};
TreeSet<Integer> ts = new TreeSet<>(com);
}
// Lambda 表达式
@Test
public void test2() {
Comparator<Integer> com = (x, y) -> Integer.compare(x, y);
TreeSet<Integer> ts = new TreeSet<>(com);
}
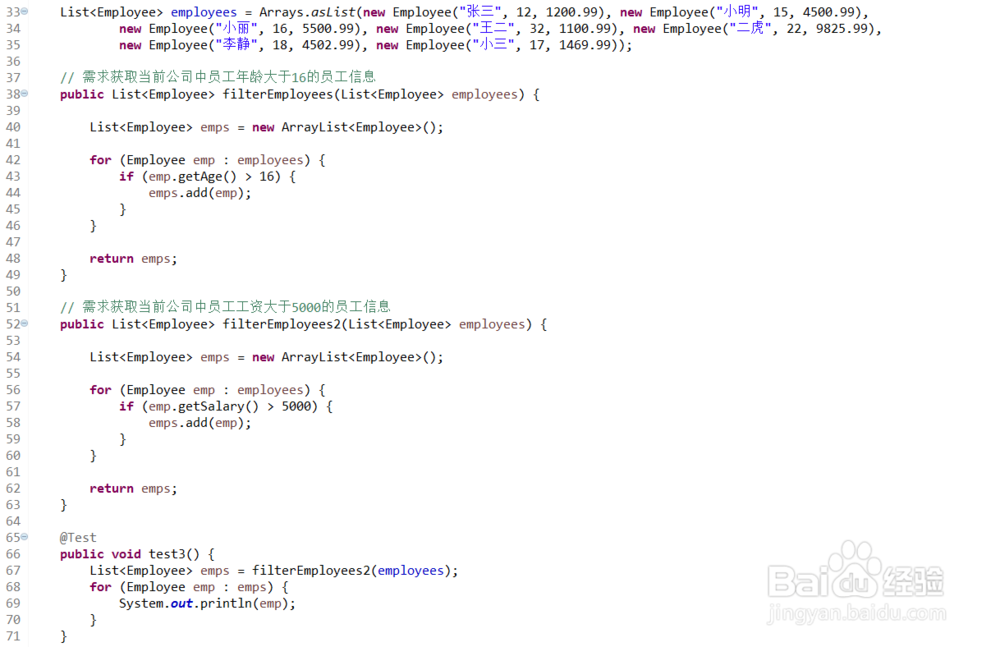
List<Employee> employees = Arrays.asList(new Employee("张三", 12, 1200.99), new Employee("小明", 15, 4500.99),
new Employee("小丽", 16, 5500.99), new Employee("王二", 32, 1100.99), new Employee("二虎", 22, 9825.99),
new Employee("李静", 18, 4502.99), new Employee("小三", 17, 1469.99));
// 需求获取当前公司中员工年龄大于16的员工信息
public List<Employee> filterEmployees(List<Employee> employees) {
List<Employee> emps = new ArrayList<Employee>();
for (Employee emp : employees) {
if (emp.getAge() > 16) {
emps.add(emp);
}
}
return emps;
}
// 需求获取当前公司中员工工资大于5000的员工信息
public List<Employee> filterEmployees2(List<Employee> employees) {
List<Employee> emps = new ArrayList<Employee>();
for (Employee emp : employees) {
if (emp.getSalary() > 5000) {
emps.add(emp);
}
}
return emps;
}
@Test
public void test3() {
List<Employee> emps = filterEmployees2(employees);
for (Employee emp : emps) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
// 优化方式一:使用设计模式-策略设计模式
public List<Employee> filterEmployee(List<Employee> employees, MyPredicate<Employee> mp) {
List<Employee> emps = new ArrayList<Employee>();
for (Employee emp : employees) {
if (mp.test(emp)) {
emps.add(emp);
}
}
return emps;
}
@Test
public void test4() {
// List<Employee> emps = filterEmployee(employees, new FilterEmployeeByAge());
List<Employee> emps = filterEmployee(employees, new FilterEmployeeBySalary());
for (Employee emp : emps) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
// 优化方式二:匿名内部类
@Test
public void test5() {
List<Employee> emps = filterEmployee(employees, new MyPredicate<Employee>() {
@Override
public boolean test(Employee t) {
return t.getAge() < 16;
}
});
for (Employee emp : emps) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
// 优化方式三:lambda表达式
@Test
public void test6() {
List<Employee> emps = filterEmployee(employees, (e) -> e.getAge() > 17);
for (Employee emp : emps) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
// 优化方式四:streamAPI
@Test
public void test7() {
employees.stream().filter((e) -> e.getAge() > 17).forEach(System.out::println);
employees.stream().map(Employee::getName).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}


2、Lambda表达式基础语法:
package com.sgg.lambda2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import org.junit.Test;
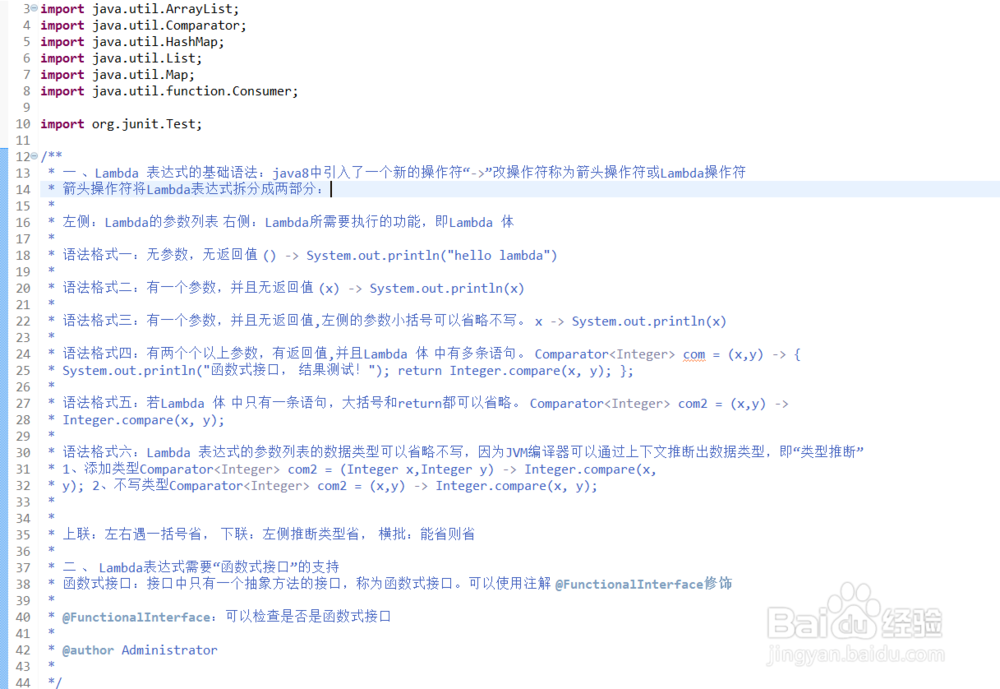
/**
* 一 、Lambda 表达式的基础语法:java8中引入了一个新的操作符“->”改操作符称为箭头操作符或Lambda操作符
* 箭头操作符将Lambda表达式拆分成两部分:
*
* 左侧:Lambda的参数列表 右侧:Lambda所需要执行的功能,即Lambda 体
*
* 语法格式一:无参数,无返回值 () -> System.out.println("hello lambda")
*
* 语法格式二:有一个参数,并且无返回值 (x) -> System.out.println(x)
*
* 语法格式三:有一个参数,并且无返回值,左侧的参数小括号可以省略不写。 x -> System.out.println(x)
*
* 语法格式四:有两个个以上参数,有返回值,并且Lambda 体 中有多条语句。 Comparator<Integer> com = (x,y) -> {
* System.out.println("函数式接口, 结果测试!"); return Integer.compare(x, y); };
*
* 语法格式五:若Lambda 体 中只有一条语句,大括号和return都可以省略。 Comparator<Integer> com2 = (x,y) ->
* Integer.compare(x, y);
*
* 语法格式六:Lambda 表达式的参数列表的数据类型可以省略不写,因为JVM编译器可以通过上下文推断出数据类型,即“类型推断”
* 1、添加类型Comparator<Integer> com2 = (Integer x,Integer y) -> Integer.compare(x,
* y); 2、不写类型Comparator<Integer> com2 = (x,y) -> Integer.compare(x, y);
*
*
* 上联:左右遇一括号省, 下联:左侧推断类型省, 横批:能省则省
*
* 二 、 Lambda表达式需要“函数式接口”的支持
* 函数式接口:接口中只有一个抽象方法的接口,称为函数式接口。可以使用注解 @FunctionalInterface修饰
*
* @FunctionalInterface:可以检查是否是函数式接口
*
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class TestLambda2 {
@Test
public void test1() {
int sum = 9;// jdk1.7 以前必须写final jdk1.8之后可以省略
Runnable r1 = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello world!" + sum);
}
};
r1.run();
System.out.println("-----------------------------------");
Runnable r2 = () -> System.out.println("hello lambda");
r2.run();
}
@Test
public void test2() {
Consumer<String> com = (x) -> System.out.println(x);
com.accept("我爱学习java!");
Consumer<String> con = x -> System.out.println(x);
con.accept("我爱学习java!");
}
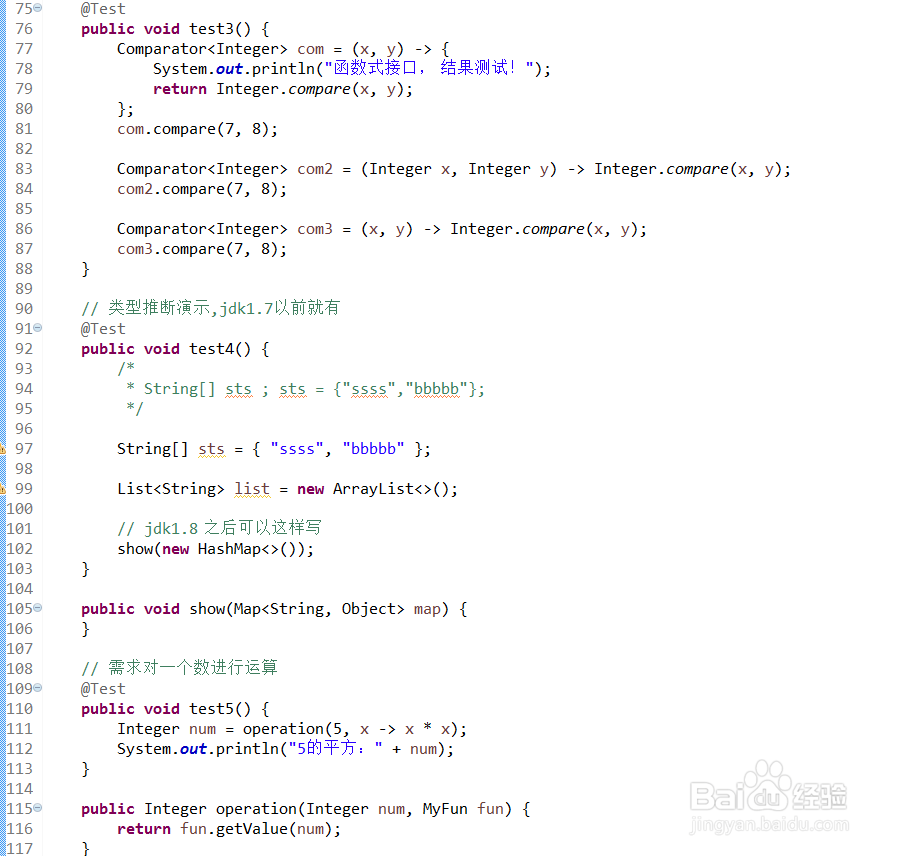
@Test
public void test3() {
Comparator<Integer> com = (x, y) -> {
System.out.println("函数式接口, 结果测试!");
return Integer.compare(x, y);
};
com.compare(7, 8);
Comparator<Integer> com2 = (Integer x, Integer y) -> Integer.compare(x, y);
com2.compare(7, 8);
Comparator<Integer> com3 = (x, y) -> Integer.compare(x, y);
com3.compare(7, 8);
}
// 类型推断演示,jdk1.7以前就有
@Test
public void test4() {
/*
* String[] sts ; sts = {"ssss","bbbbb"};
*/
String[] sts = { "ssss", "bbbbb" };
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// jdk1.8 之后可以这样写
show(new HashMap<>());
}
public void show(Map<String, Object> map) {
}
// 需求对一个数进行运算
@Test
public void test5() {
Integer num = operation(5, x -> x * x);
System.out.println("5的平方:" + num);
}
public Integer operation(Integer num, MyFun fun) {
return fun.getValue(num);
}
}

3、Lambda表达式练习:
package com.sgg.lambda3;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.sgg.lambda1.Employee;
public class TestLambda3 {
List<Employee> employees = Arrays.asList(new Employee("张三", 12, 1200.99), new Employee("小明", 15, 4500.99),
new Employee("小丽", 16, 5500.99), new Employee("王二", 32, 1100.99), new Employee("二虎", 22, 9825.99),
new Employee("李静", 18, 4502.99), new Employee("小三", 17, 1469.99));
// 练习1、调用Collections.sort方法,通过定制排序比较Employee(先按年龄大小年龄相同按照姓名比较)
@Test
public void test1() {
Collections.sort(employees, (e1, e2) -> {
if (e1.getAge() == e2.getAge()) {
// return e1.getName().compareTo(e2.getName());
// 逆向排序
return -e1.getName().compareTo(e2.getName());
} else {
// return Integer.compare(e1.getAge(),e2.getAge());
// 逆向排序
return -Integer.compare(e1.getAge(), e2.getAge());
}
});
for (Employee emp : employees) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
// 练习2、
// 2.1 声明函数式接口,接口中声明抽象方法,public String getValue(String str);
// 2.2 声明类TestLambda3,类中调用方法使用接口作为参数,将一个字符串转为大写,并作为方法的返回值
// 2.3 将一个字符串的第下标位置2到4之间的字符串截取
@Test
public void test2() {
String trimStr = strHandler("\t\t\t我爱学习java", str -> str.trim());
System.out.println(trimStr);
String trimStr2 = strHandler("aaaaaaaaa", str -> str.toUpperCase());
System.out.println(trimStr2);
String trimStr3 = strHandler("我爱学习java", str -> str.substring(2, 4));
System.out.println(trimStr3);
}
public String strHandler(String str, MyFunction mf) {
return mf.getValue(str);
}
// 练习3
// 3.1声明一个带两个泛型的函数式接口,泛型类型<T,R>,T为参数,R为返回值
// 3.2 接口中声明对应的抽象方法
// 3.3 在TestLambda3类中声明方法,使用接口作为参数,计算两个long型参数的和。
// 3.4计算两个long型参数的乘积
@Test
public void test3() {
long count = op(55, 20, (l1, l2) -> l1 + l2);
System.out.println(count);
long count2 = op(55, 20, (l1, l2) -> l1 * l2);
System.out.println(count2);
}
public long op(long l1, long l2, MyFunctionLong<Long, Long> ml) {
return ml.longCount(l1, l2);
}
}


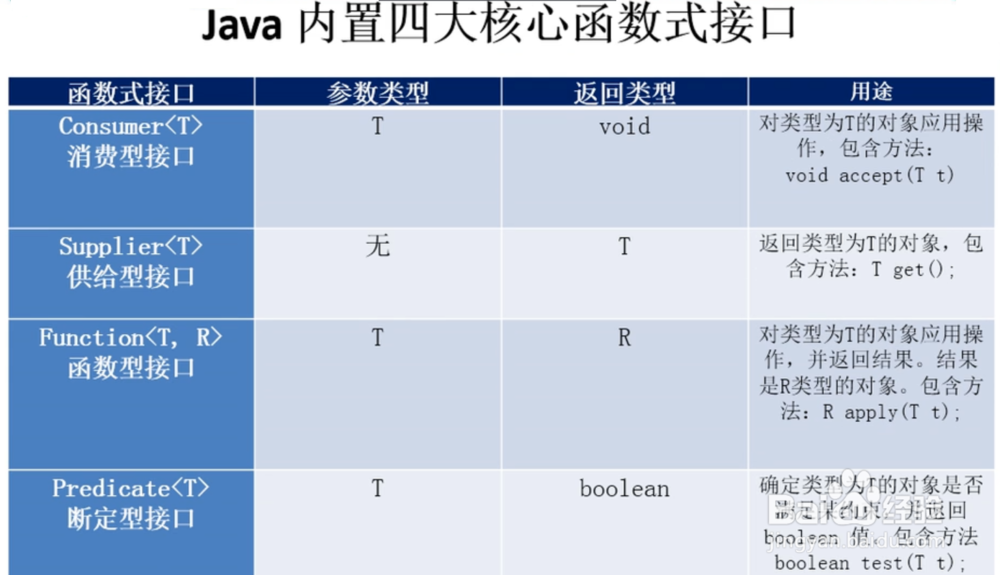
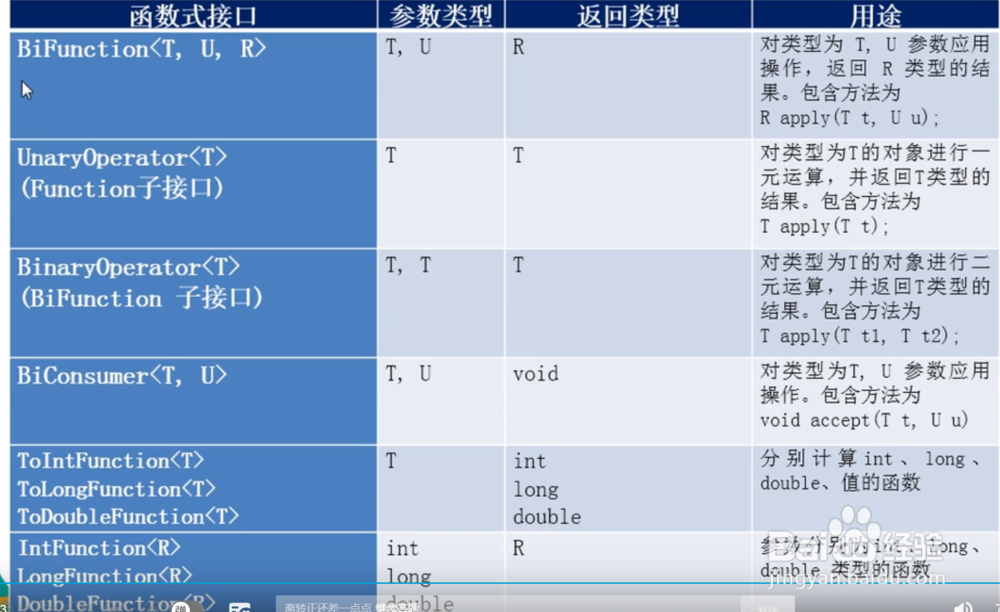
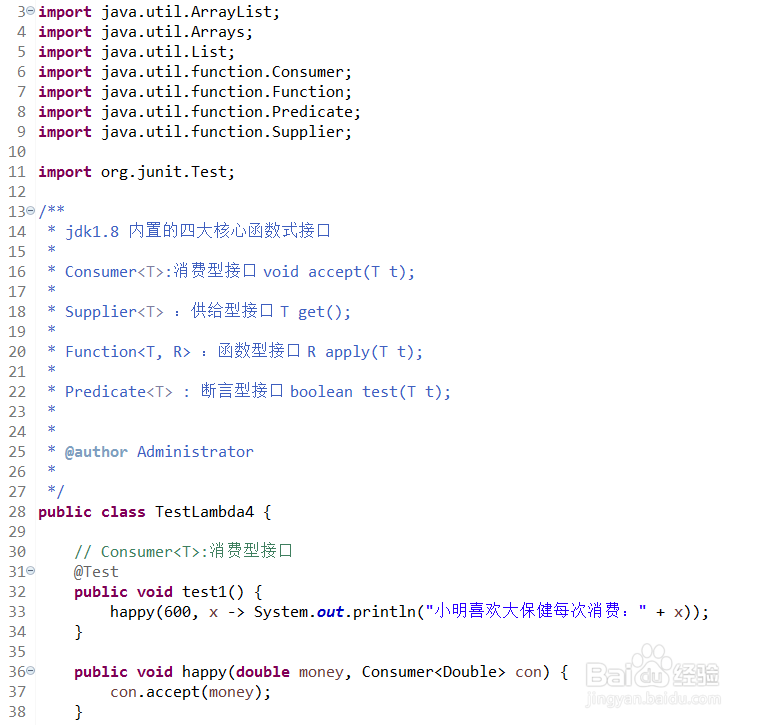
4、内置函数式接口
package com.sgg.lambda4;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* jdk1.8 内置的四大核心函数式接口
*
* Consumer<T>:消费型接口 void accept(T t);
*
* Supplier<T> :供给型接口 T get();
*
* Function<T, R> :函数型接口 R apply(T t);
*
* Predicate<T> : 断言型接口 boolean test(T t);
*
*
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class TestLambda4 {
// Consumer<T>:消费型接口
@Test
public void test1() {
happy(600, x -> System.out.println("小明喜欢大保健每次消费:" + x));
}
public void happy(double money, Consumer<Double> con) {
con.accept(money);
}
// Supplier<T> :供给型接口
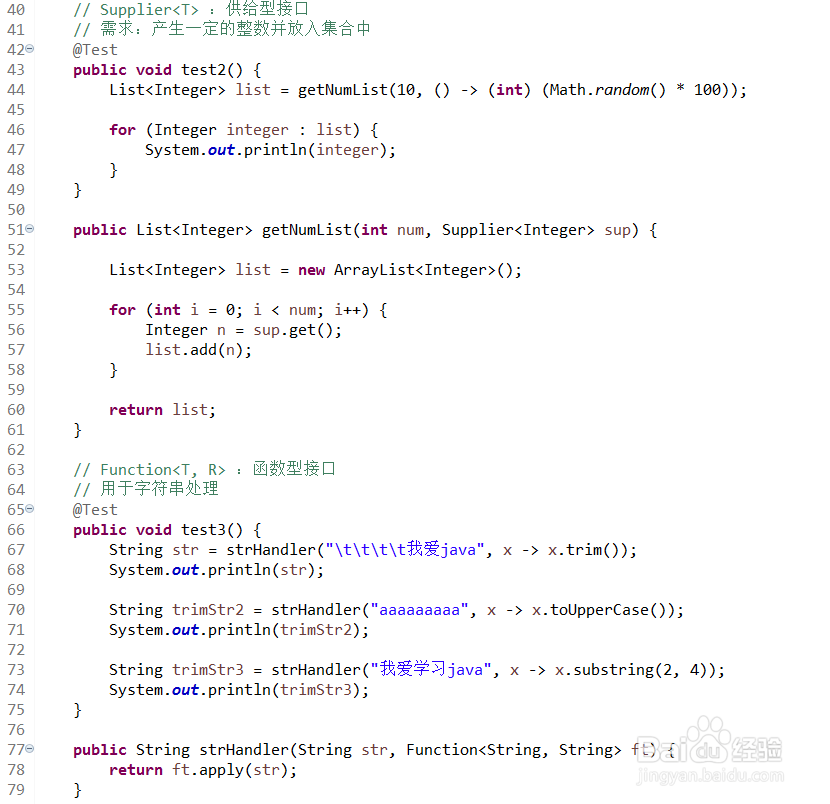
// 需求:产生一定的整数并放入集合中
@Test
public void test2() {
List<Integer> list = getNumList(10, () -> (int) (Math.random() * 100));
for (Integer integer : list) {
System.out.println(integer);
}
}
public List<Integer> getNumList(int num, Supplier<Integer> sup) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
Integer n = sup.get();
list.add(n);
}
return list;
}
// Function<T, R> :函数型接口
// 用于字符串处理
@Test
public void test3() {
String str = strHandler("\t\t\t\t我爱java", x -> x.trim());
System.out.println(str);
String trimStr2 = strHandler("aaaaaaaaa", x -> x.toUpperCase());
System.out.println(trimStr2);
String trimStr3 = strHandler("我爱学习java", x -> x.substring(2, 4));
System.out.println(trimStr3);
}
public String strHandler(String str, Function<String, String> ft) {
return ft.apply(str);
}
// Predicate<T> : 断言型接口
// 需求:将满足条件的字符串放入集合中去
@Test
public void test4() {
List<String> lists = Arrays.asList("sdsad", "我爱java", "我爱祖国", "我爱人民");
List<String> listStr = filterStr(lists, x -> x.length() > 3);
for (String string : listStr) {
System.out.println(string);
}
}
public List<String> filterStr(List<String> listStr, Predicate<String> pre) {
List<String> lists = new ArrayList<>();
for (String str : listStr) {
if (pre.test(str)) {
lists.add(str);
}
}
return lists;
}
}

5、方法引用
package com.sgg.lambda5;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.function.BiPredicate;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.sgg.lambda1.Employee;
/**
* 一 、方法引用:若Lambda体中内容有方法已经实现了,我们可以使用“方法引用” (可以理解为方法引用是Lambda表达式的另一种表现形式)
*
* 主要有三种语法格式:
*
* 对象::实例方法名
*
* 类::静态方法名
*
* 类::实例方法名
*
* 注意: Lambda体中调用方法的参数列表与返回值类型,要与函数式接口中抽象方法的函数列表和返回值类型一致!
* 若Lambda参数列表中的第一参数是实例方法的调用者,第二参数是实例方法的参数时,可以使用ClassName::method
*
* 二 、构造器引用
*
* 格式: ClassName::new
*
* 注意:需要调用的构造器的参数列表要与函数式接口中抽象方法的参数列表保持一致!
*
* 三 、数组引用
*
* Type::new;
*
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class TestMethodRef {
// 对象::实例方法名
@Test
public void test1() {
// 第一种
Consumer<String> con2 = (x) -> System.out.println(x);
// 第二种
PrintStream ps1 = System.out;
Consumer<String> con1 = (x) -> ps1.println(x);
// 第三种
PrintStream ps = System.out;
Consumer<String> con3 = ps::println;
con3.accept("我爱世界!");
}
@Test
public void test2() {
Employee emp = new Employee();
Supplier<String> su = () -> emp.getName();
String st = su.get();
System.out.println(st);
Employee emp2 = new Employee();
Supplier<Integer> su2 = () -> emp2.getAge();
Integer num = su2.get();
System.out.println(num);
}
// 类::静态方法名
@Test
public void test3() {
Comparator<Integer> com1 = (x, y) -> Integer.compare(x, y);
Comparator<Integer> com2 = Integer::compare;
}
// 类::实例方法名
@Test
public void test4() {
BiPredicate<String, String> bp1 = (x, y) -> x.equals(y);
BiPredicate<String, String> bp2 = String::equals;
}
// 类::构造器引用
@Test
public void test5() {
Supplier<Employee> su1 = () -> new Employee();
Supplier<Employee> su2 = Employee::new;
Employee em = su2.get();
System.out.println(em);
}
@Test
public void test6() {
Function<String, Employee> fun = (x) -> new Employee(x);
Employee em = fun.apply("小丽");
System.out.println(em);
}
// 数组引用
@Test
public void test7() {
Function<Integer, String[]> fun1 = (x) -> new String[x];
String[] sts1 = fun1.apply(10);
System.out.println(sts1.length);
Function<Integer, String[]> fun2 = String[]::new;
String[] sts2 = fun2.apply(20);
System.out.println(sts2.length);
}
}


6、源码地址:
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1DpGycBWEJ43kXpuOgkzDQQ
提取码: umxt