Java核心API之异常处理(下)
1、获取Exception信息常用的方法
1、printStackTrace()
该方法可以输出错误信息,可以跟踪异常事件发生的详细位置,即Java堆栈的内容。该方法是void printStackTrace()
实例代码如下:
/*
* 使用printStackTrace()方法
*/
@Test
public void testPrintStackTrace(){ FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("test.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
if(fis!=null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
分析:上述代码显示的错误信息可以见下图,为什么用printStackTrace()产生的信息这么多呢?其实Java运行时,JVM将数据信息方在堆栈中,出现的错误信息从下到上本质上是JVM运行到异常代码出错的执行顺序,也就是说找异常错误的原因可以在异常信息中从下至上查找。

2、getMessage()
该方法可以得到有关异常事件的信息。该方法是String getMessage()
示例代码如下:
/*
* 使用printStackTrace()方法
*/
@Test
public void testPrintStackTrace(){
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("test.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally{
if(fis!=null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
分析:String getMessage()返回值是字符串,记录程序执行时出错的原因,不像printStackTrace()满篇红,容易让人接受。

3、getCause()
该方法是获取异常出现的原因。
有的时候,一个异常引起另一个异常的抛出,Java库和开源代码将一种异常包装成新的异常。这时,可以通过getCause()方法打印异常日志,可以对产生异常的底层原因提供更多的信息。便于开发人员对代码的调试。
4、自定义异常需要继承Exception类
代码片段如下:
class 自定义异常类的名称 extends Exception{
......
}
实例代码如下:
1、自定义异常
public class CustomedException extends Exception { public CustomedException() {
super();
}
public CustomedException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) {
super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace);
}
public CustomedException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public CustomedException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public CustomedException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}}

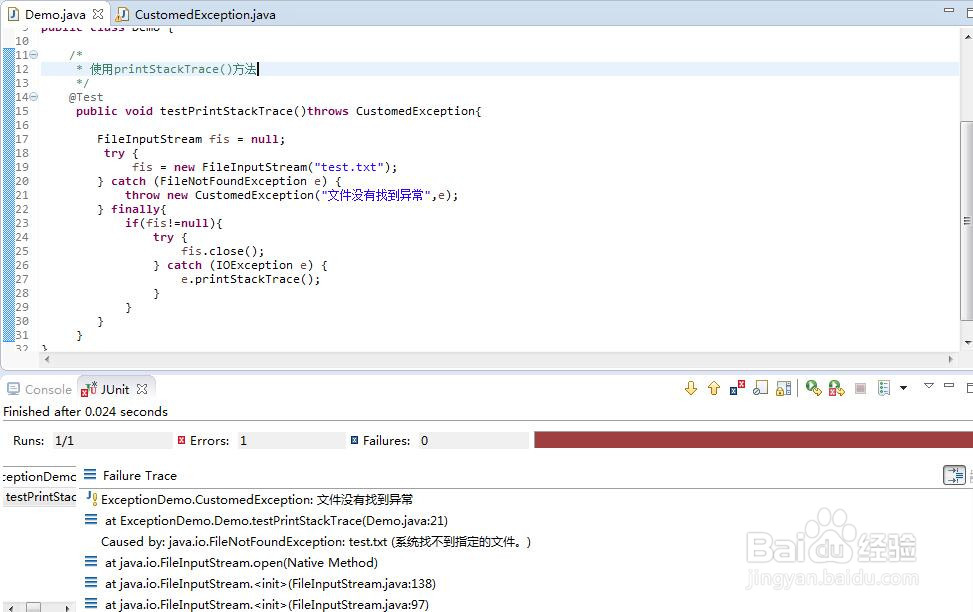
5、读取文件抛出异常demo
public class Demo { /*
* 使用printStackTrace()方法
*/
@Test
public void testPrintStackTrace()throws CustomedException{ FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("test.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new CustomedException("文件没有找到异常",e);
} finally{
if(fis!=null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
分析:拷贝上述代码,运行测试,实际了解自定义异常的用法