linux线程优先级设置
1、Linux线程优先级设置:
首先,可以通过以下两个函数来获得线程可以设置的最高和最低优先级,函数中的策略即上述三种策略的宏定义:
int sched_get_priority_max(int policy); int sched_get_priority_min(int policy);

2、注意:SCHED_OTHER 是不支持优先级使用的,而 SCHED_FIFO 和 SCHED_RR 支持优先级的使用,他们分别为1和99,数值越大优先级越高。
设置和获取优先级通过以下两个函数:
int pthread_attr_setschedparam(pthread_attr_t *attr, const struct sched_param *param);int pthread_attr_getschedparam(const pthread_attr_t *attr, struct sched_param *param); param.sched_priority = 51; //设置优先级

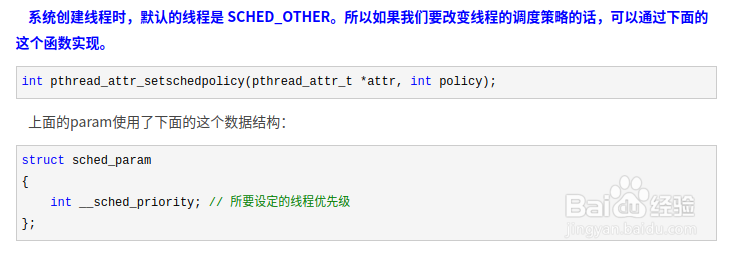
3、系统创建线程时,默认的线程是 SCHED_OTHER。所以如果我们要改变线程的调度策略的话,可以通过下面的这个函数实现。
int pthread_attr_setschedpolicy(pthread_attr_t *attr, int policy);
上面的param使用了下面的这个数据结构:
struct sched_param{
int __sched_priority; // 所要设定的线程优先级
};
4、我们可以通过下面的测试程序来说明,我们自己使用的系统的支持的优先级:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sched.h>
#include <assert.h>
static int api_get_thread_policy (pthread_attr_t *attr)
{
int policy;
int rs = pthread_attr_getschedpolicy (attr, &policy);
assert (rs == 0);
switch (policy)
{
case SCHED_FIFO:
printf ("policy = SCHED_FIFO\n");
break;
case SCHED_RR:
printf ("policy = SCHED_RR");
break;
case SCHED_OTHER:
printf ("policy = SCHED_OTHER\n");
break;
default:
printf ("policy = UNKNOWN\n");
break;
}
return policy;
}
static void api_show_thread_priority (pthread_attr_t *attr,int policy)
{
int priority = sched_get_priority_max (policy);
assert (priority != -1);
printf ("max_priority = %d\n", priority);
priority = sched_get_priority_min (policy);
assert (priority != -1);
printf ("min_priority = %d\n", priority);
}
static int api_get_thread_priority (pthread_attr_t *attr)
{
struct sched_param param;
int rs = pthread_attr_getschedparam (attr, ¶m);
assert (rs == 0);
printf ("priority = %d\n", param.__sched_priority);
return param.__sched_priority;
}
static void api_set_thread_policy (pthread_attr_t *attr,int policy)
{
int rs = pthread_attr_setschedpolicy (attr, policy);
assert (rs == 0);
api_get_thread_policy (attr);
}
int main(void)
{
pthread_attr_t attr; // 线程属性
struct sched_param sched; // 调度策略
int rs;
/*
* 对线程属性初始化
* 初始化完成以后,pthread_attr_t 结构所包含的结构体
* 就是操作系统实现支持的所有线程属性的默认值
*/
rs = pthread_attr_init (&attr);
assert (rs == 0); // 如果 rs 不等于 0,程序 abort() 退出
/* 获得当前调度策略 */
int policy = api_get_thread_policy (&attr);
/* 显示当前调度策略的线程优先级范围 */
printf ("Show current configuration of priority\n");
api_show_thread_priority(&attr, policy);
/* 获取 SCHED_FIFO 策略下的线程优先级范围 */
printf ("show SCHED_FIFO of priority\n");
api_show_thread_priority(&attr, SCHED_FIFO);
/* 获取 SCHED_RR 策略下的线程优先级范围 */
printf ("show SCHED_RR of priority\n");
api_show_thread_priority(&attr, SCHED_RR);
/* 显示当前线程的优先级 */
printf ("show priority of current thread\n");
int priority = api_get_thread_priority (&attr);
/* 手动设置调度策略 */
printf ("Set thread policy\n");
printf ("set SCHED_FIFO policy\n");
api_set_thread_policy(&attr, SCHED_FIFO);
printf ("set SCHED_RR policy\n");
api_set_thread_policy(&attr, SCHED_RR);
/* 还原之前的策略 */
printf ("Restore current policy\n");
api_set_thread_policy (&attr, policy);
/*
* 反初始化 pthread_attr_t 结构
* 如果 pthread_attr_init 的实现对属性对象的内存空间是动态分配的,
* phread_attr_destory 就会释放该内存空间
*/
rs = pthread_attr_destroy (&attr);
assert (rs == 0);
return 0;
}

5、下面是测试程序的运行结果:
policy=SCHED_OTHER
Show current configuration of priority
max_priority=0
min_priority=0
show SCHED_FIFO of priority
max_priority=99
min_priority=1
show SCHED_RR of priority
max_priority=99
min_priority=1
show priority of current thread
priority=0Set thread policy
set SCHED_FIFO policy
policy= SCHED_FIFO
set SCHED_RR policy
policy= SCHED_RRRestore current policy
policy=SCHED_OTHER
