如何在Python里进行文件的读取和写入
1、file1 = open('abc.txt', 'r')
print(file1.name)
file1.close()
直接用open,定义只读模式,可以查看文件的名字,记得要关闭文件。

2、file1 = open('abc.txt')
print(file1.mode)
file1.close()
默认的是只读模式,用mode可以查看。

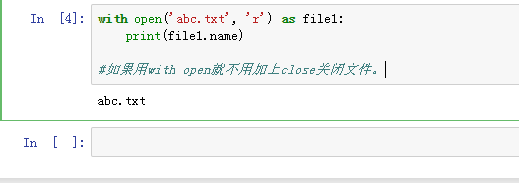
3、with open('abc.txt', 'r') as file1:
print(file1.name)
如果用with open就不用加上close关闭文件
4、with open('abc.txt', 'r') as file1:
print(file1.name)
print(file1.closed)
用closed验证一下是否已经关闭了文件。
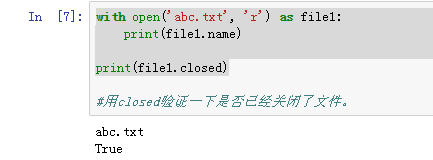
5、with open('abc.txt', 'r') as file1:
print(file1.name)
print(file1.read())
关闭了的文件就不能直接读取了。
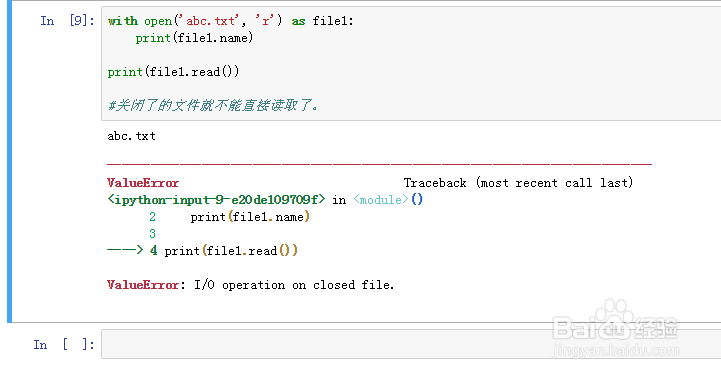
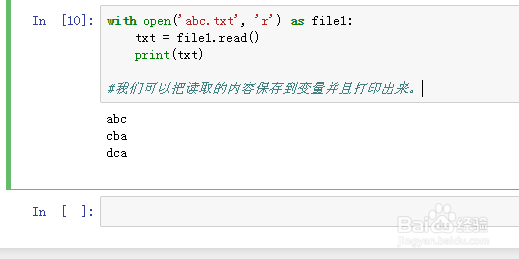
6、with open('abc.txt', 'r') as file1:
txt = file1.read()
print(txt)
我们可以把读取的内容保存到变量并且打印出来。
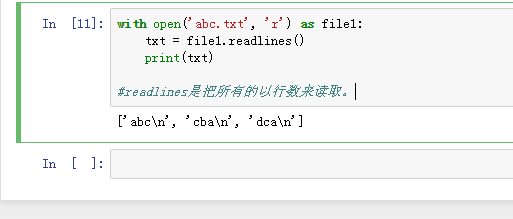
7、with open('abc.txt', 'r') as file1:
txt = file1.readlines()
print(txt)
readlines是把所有的以行数来读取。
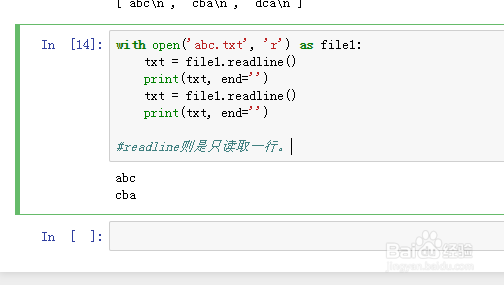
8、with open('abc.txt', 'r') as file1:
txt = file1.readline()
print(txt, end='')
txt = file1.readline()
print(txt, end='')
readline则是只读取一行。
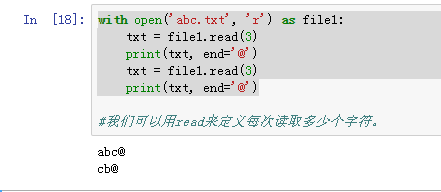
9、with open('abc.txt', 'r') as file1:
txt = file1.read(3)
print(txt, end='@')
txt = file1.read(3)
print(txt, end='@')
我们可以用read来定义每次读取多少个字符。
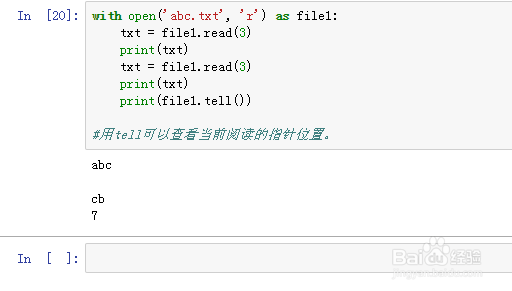
10、with open('abc.txt', 'r') as file1:
txt = file1.read(3)
print(txt)
txt = file1.read(3)
print(txt)
print(file1.tell())
用tell可以查看当前阅读的指针位置。
11、with open('abc.txt', 'r') as file1:
txt = file1.read(3)
print(txt)
file1.seek(0)
txt = file1.read(3)
print(txt)
用seek可以让指针到指定的位置,比如0就是从头来。

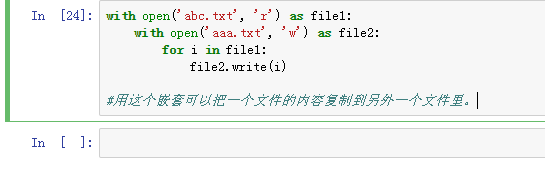
12、with open('abc.txt', 'r') as file1:
with open('aaa.txt', 'w') as file2:
for i in file1:
file2.write(i)
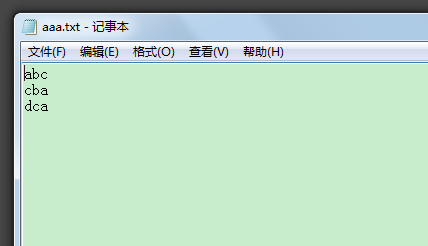
用这个嵌套可以把一个文件的内容复制到另外一个文件里。