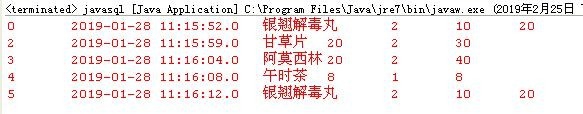
java-sql:查询表中的数据
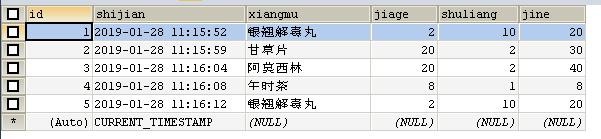
1、登录mysql在test数据库中新建一个表shoufei,接下来java连接mysql数据库在shoufe表的数据显示出来:
Create Table
CREATE TABLE `shoufei` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `shijian` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, `xiangmu` varchar(20) NOT NULL, `jiage` float NOT NULL, `shuliang` int(11) NOT NULL, `jine` float DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`)) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
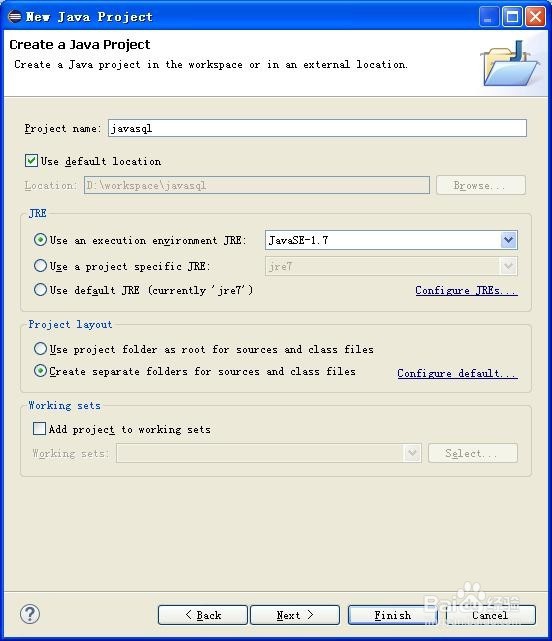
2、在eclipse中新建一个java项目,项目名字为javasql。
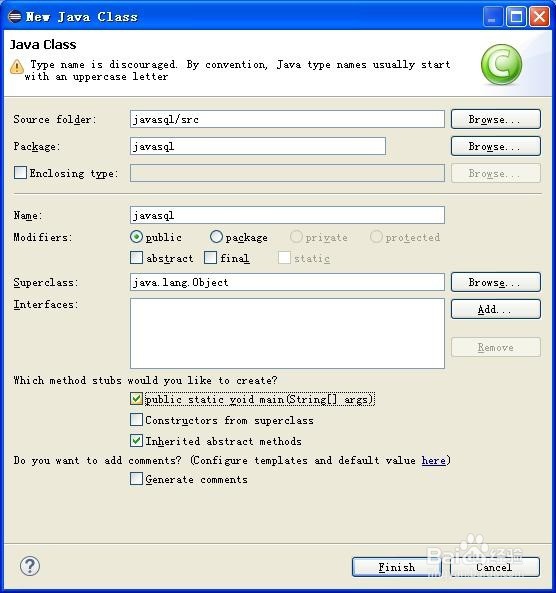
3、在javasql项目中新建一个javasql类,带有main主函数的类。
4、在javasql项目中增加mysql驱动。
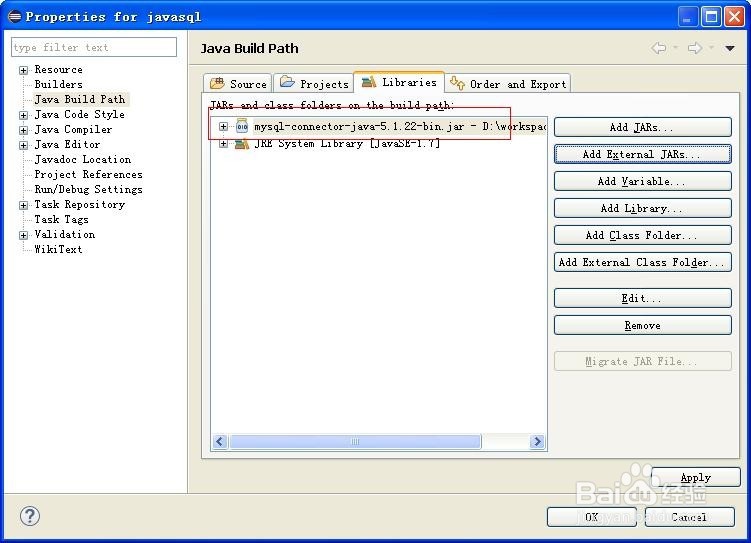
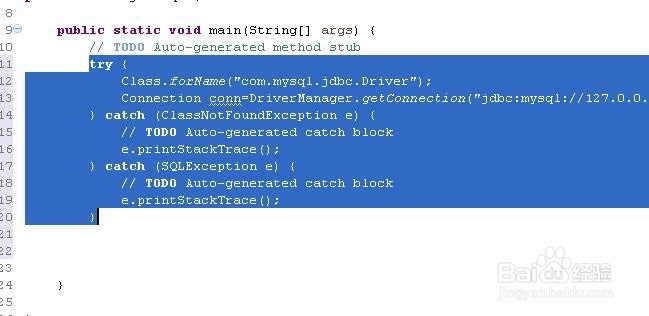
5、打开javasql.java这个文件,在main方法中连接mysql数据库。
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8;","root","123456");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
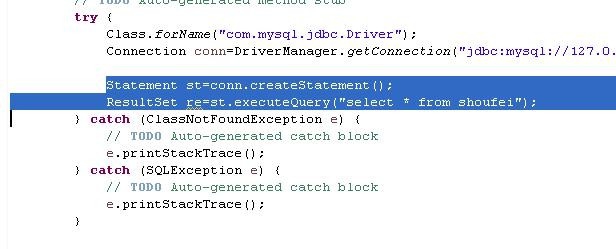
6、定义java-sql语句的声明,把sql返回记录集存储在ResultSet类型的变量中。
Statement st=conn.createStatement();
ResultSet re=st.executeQuery("select * from shoufei");
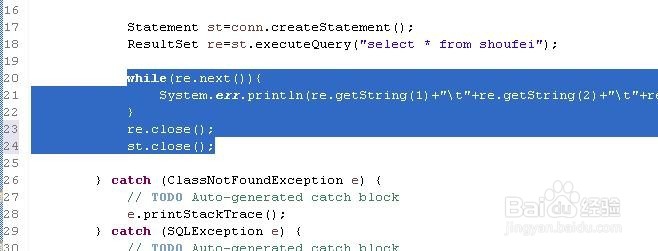
7、现在把shoufei表中的数据打印出来:
while(re.next()){
System.err.println(re.getString(1)+"\t"+re.getString(2)+"\t"+re.getString(3)+"\t"+re.getString(4)+"\t"+re.getString(5)+"\t"+re.getString(6));
}
re.close();
st.close();
8、把运行项目把表中的数据打印到屏幕上。